NASA Tests Drones to Provide Micrometeorology, Aid in Fire Response
In Aug. 2024, a team of NASA researchers and partners gathered in Missoula, to test new drone-based technology for localized forecasting, or micrometeorology. Researchers attached wind sensors to a drone, NASA’s Alta X quadcopter, aiming to provide precise and sustainable meteorological data to help predict fire behavior. Wildfires are increasing in number and severity around […]

NASA Tests Drones to Provide Micrometeorology, Aid in Fire Response

In Aug. 2024, a team of NASA researchers and partners gathered in Missoula, to test new drone-based technology for localized forecasting, or micrometeorology. Researchers attached wind sensors to a drone, NASA’s Alta X quadcopter, aiming to provide precise and sustainable meteorological data to help predict fire behavior.
Wildfires are increasing in number and severity around the world, including the United States, and wind is a major factor. It leads to unexpected and unpredictable fire growth, public threats, and fire fatalities, making micrometeorology a very effective tool to combat fire.
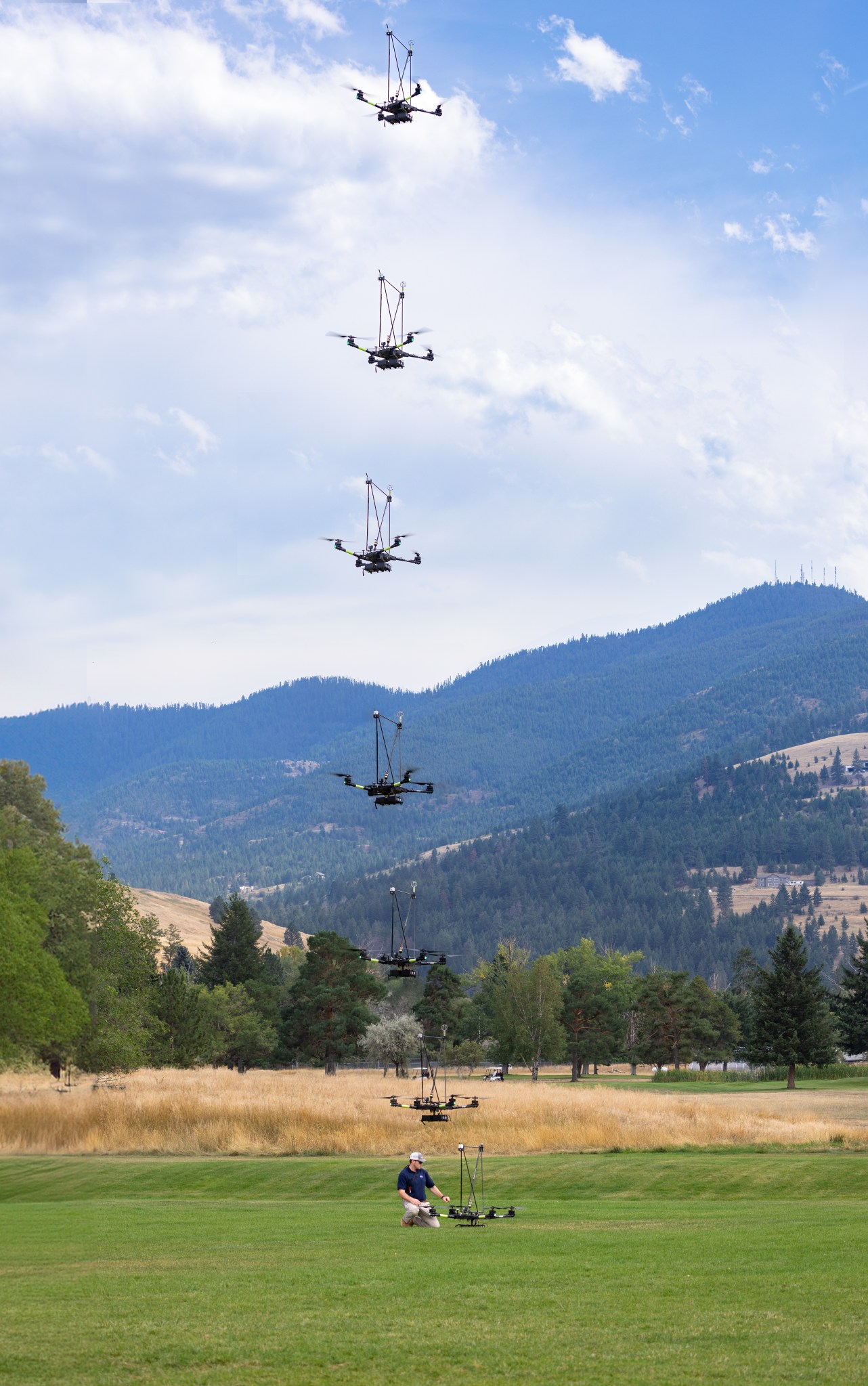

The campaign was run by NASA’s FireSense project, focused on addressing challenges in wildland fire management by putting NASA science and technology in the hands of operational agencies.
“Ensuring that the new technology will be easily adoptable by operational agencies such as the U.S. Forest Service and the National Weather Service was another primary goal of the campaign,” said Jacqueline Shuman, FireSense project scientist at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley.
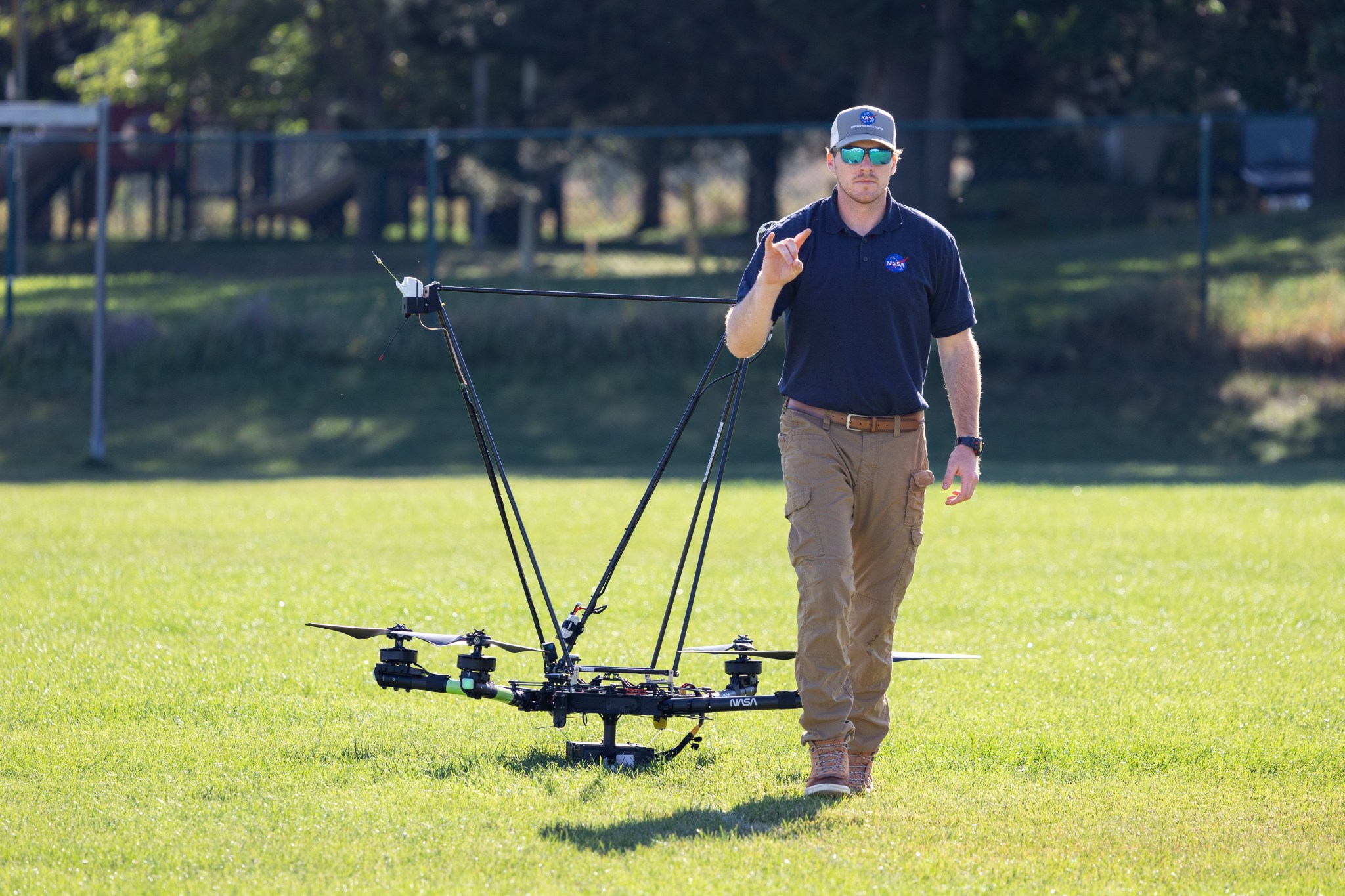
The FireSense team chose the Alta X drone because the U.S. Forest Service already has a fleet of the quadcopters and trained drone pilots, which could make integrating the needed sensors – and the accompanying infrastructure – much easier and more cost-effective for the agency.

The choice of the two sensors for the drone’s payload was also driven by their adoptability.
The first, called a radiosonde, measures wind direction and speed, humidity, temperature, and pressure, and is used daily by the National Weather Service. The other sensor, an anemometer, measures wind speed and direction, and is used at weather stations and airports around the world.
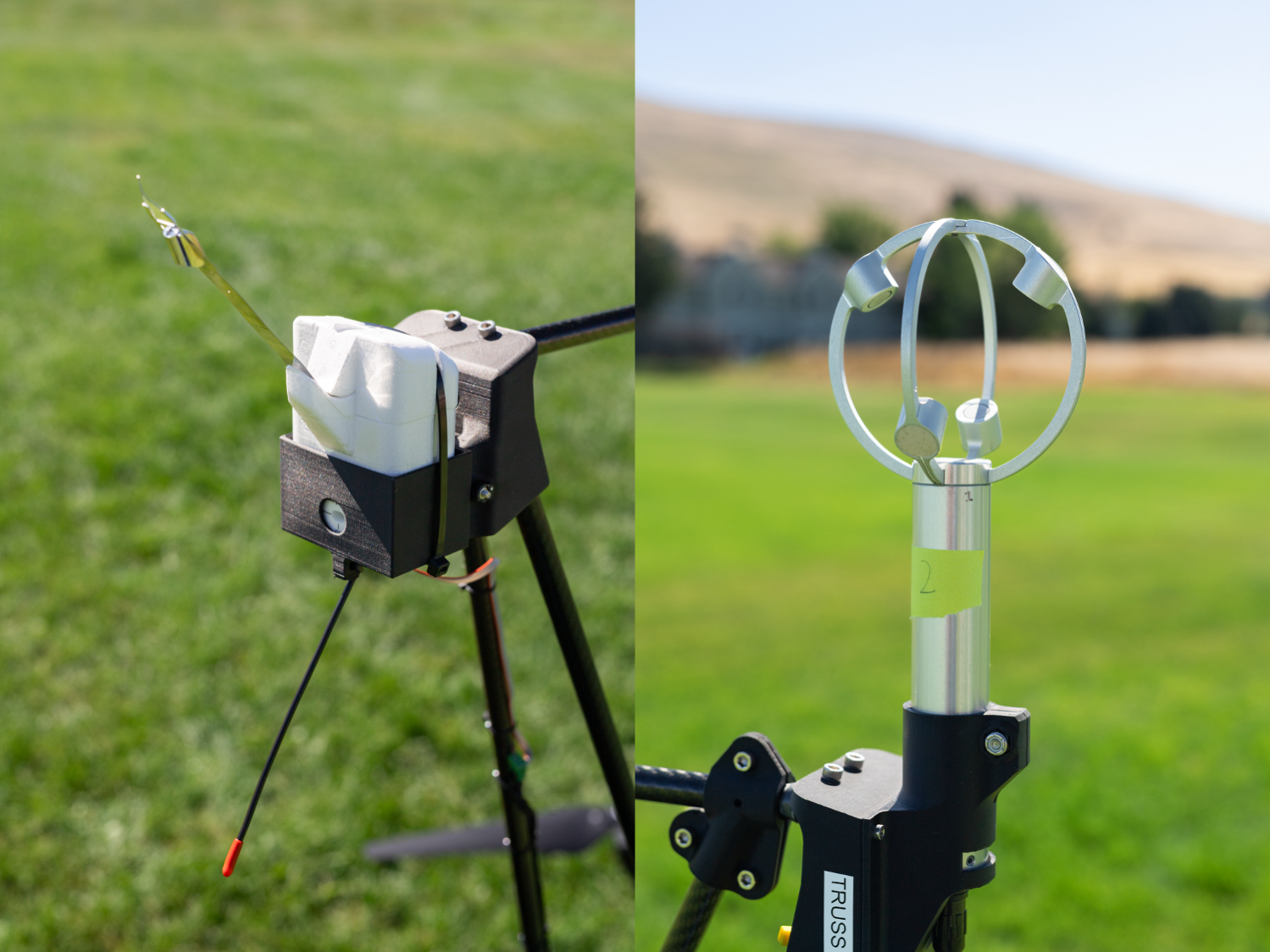

“Anemometers are everywhere, but are usually stationary,” said Robert McSwain, the FireSense uncrewed aerial system (UAS) lead, based at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. “We are taking a sensor type that is already used all over the world, and giving it wings.”
Anemometers are everywhere, but are usually stationary. We are taking a sensor type that is already used all over the world, and giving it wings.

Robert Mcswain
FireSense Uncrewed Aerial System (UAS) Lead
Both sensors create datasets that are already familiar to meteorologists worldwide, which opens up the potential applications of the platform.
Current Forecasting Methods: Weather Balloons
Traditionally, global weather forecasting data is gathered by attaching a radiosonde to a weather balloon and releasing it into the air. This system works well for regional weather forecasts. But the rapidly changing environment of wildland fire requires more recurrent, pinpointed forecasts to accurately predict fire behavior. It’s the perfect niche for a drone.
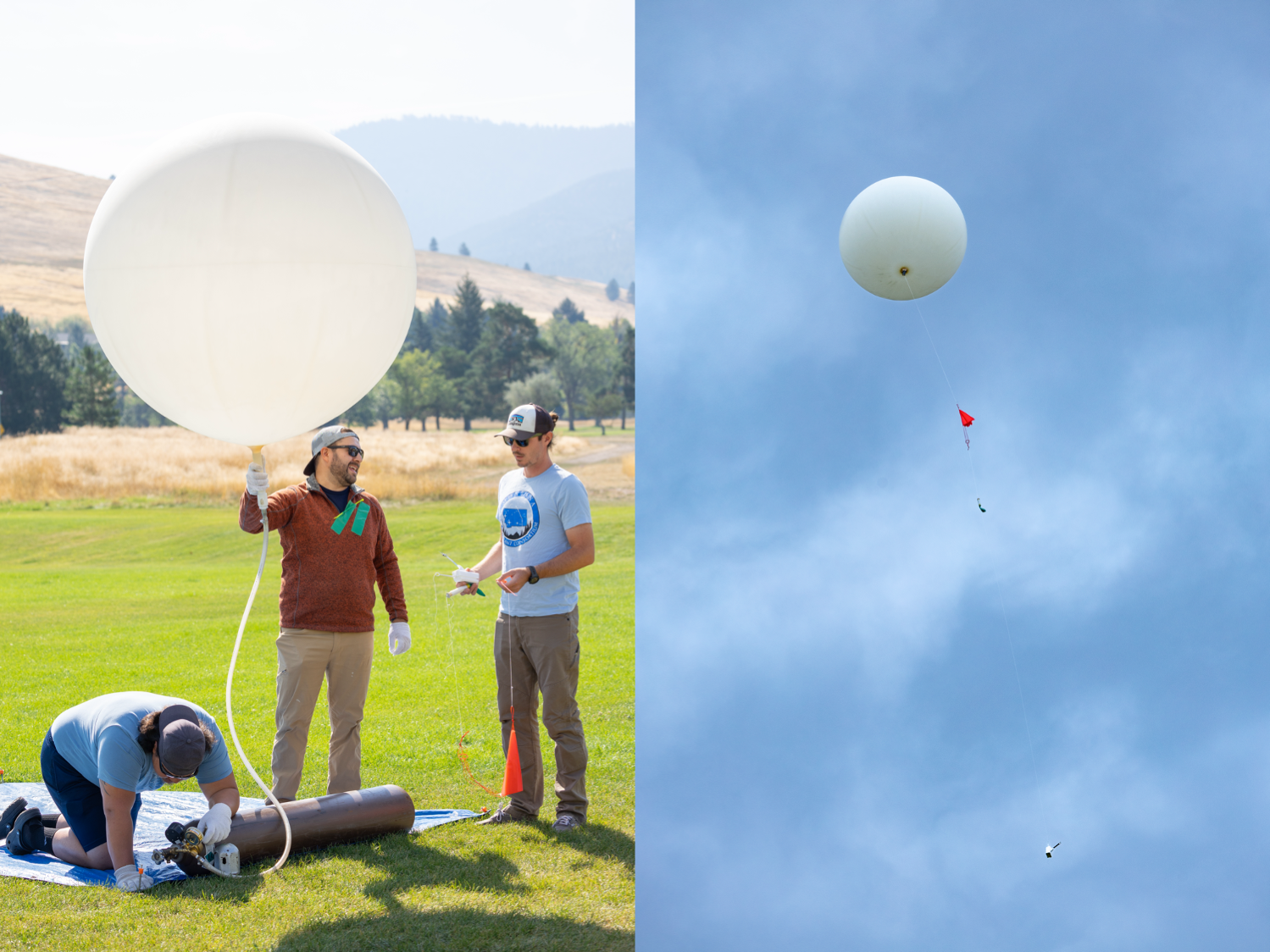

Right: One of these weather balloons lifts into the sky, with the radiosonde visible at the end of the string.
“These drones are not meant to replace the weather balloons,” said Jennifer Fowler, FireSense’s project manager at Langley. “The goal is to create a drop-in solution to get more frequent, localized data for wildfires – not to replace all weather forecasting.”
The goal is to create a drop-in solution to get more frequent, localized data for wildfires – not to replace all weather forecasting.

Jennifer Fowler
FireSense Project Manager
Drones Provide Control, Repeat Testing, Sustainability
Drones can be piloted to keep making measurements over a precise location – an on-site forecaster could fly one every couple of hours as conditions change – and gather timely data to help determine how weather will impact the direction and speed of a fire.
Fire crews on the ground may need this information to make quick decisions about where to deploy firefighters and resources, draw fire lines, and protect nearby communities.
A reusable platform, like a drone, also reduces the financial and environmental impact of forecasting flights.
“A weather balloon is going to be a one-off, and the attached sensor won’t be recovered,” Fowler said. “The instrumented drone, on the other hand, can be flown repeatedly.”
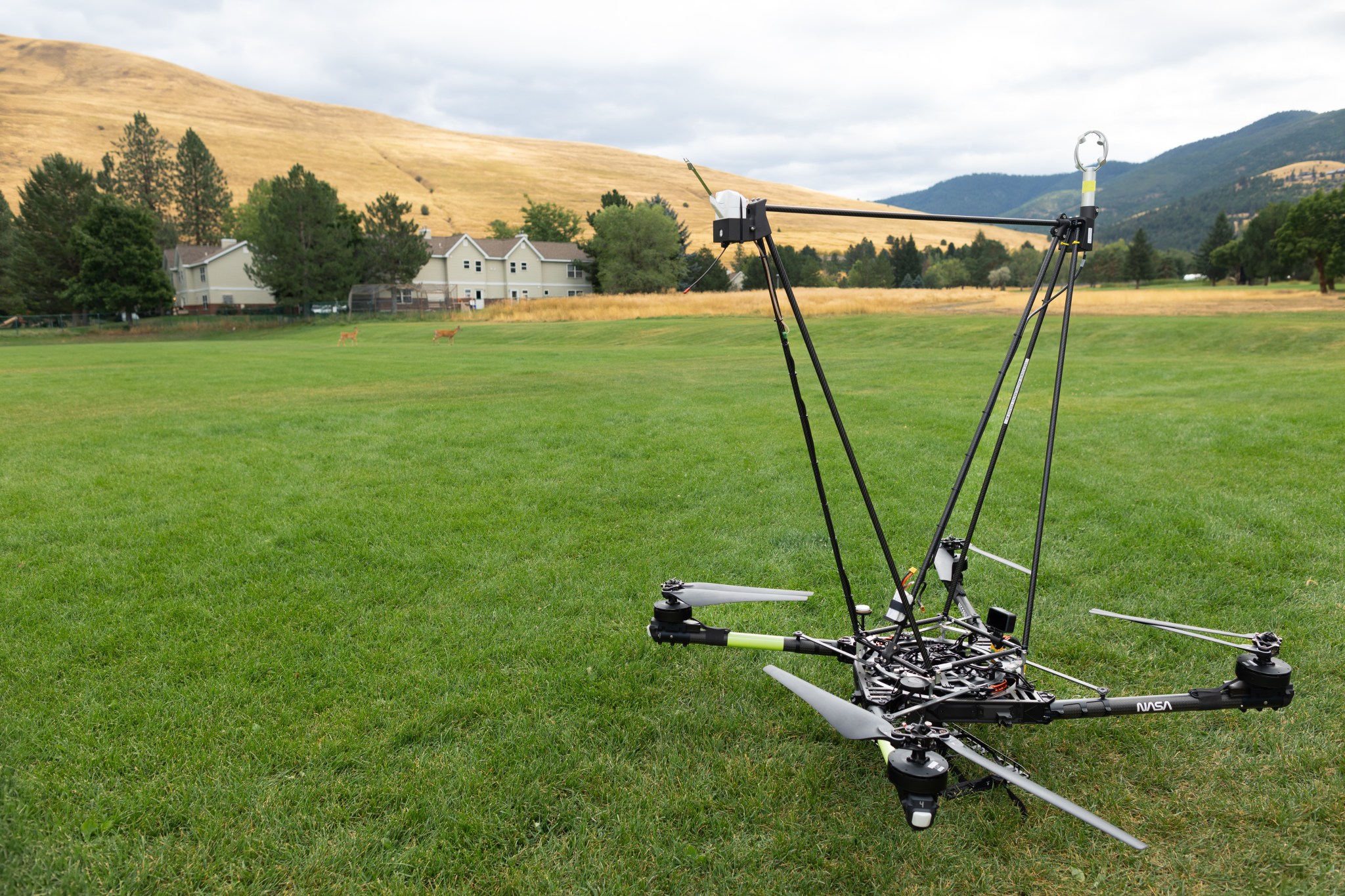

The Missoula Campaign
Before such technology can be sent out to a fire, it needs to be tested. That’s what the FireSense team did this summer.

McSwain described the conditions in Missoula as an “alignment of stars” for the research: the complex mountain terrain produces erratic, historically unpredictable winds, and the sparsity of monitoring instruments on the ground makes weather forecasting very difficult. During the three-day campaign, several fires burned nearby, which allowed researchers to test how the drones performed in smokey conditions.
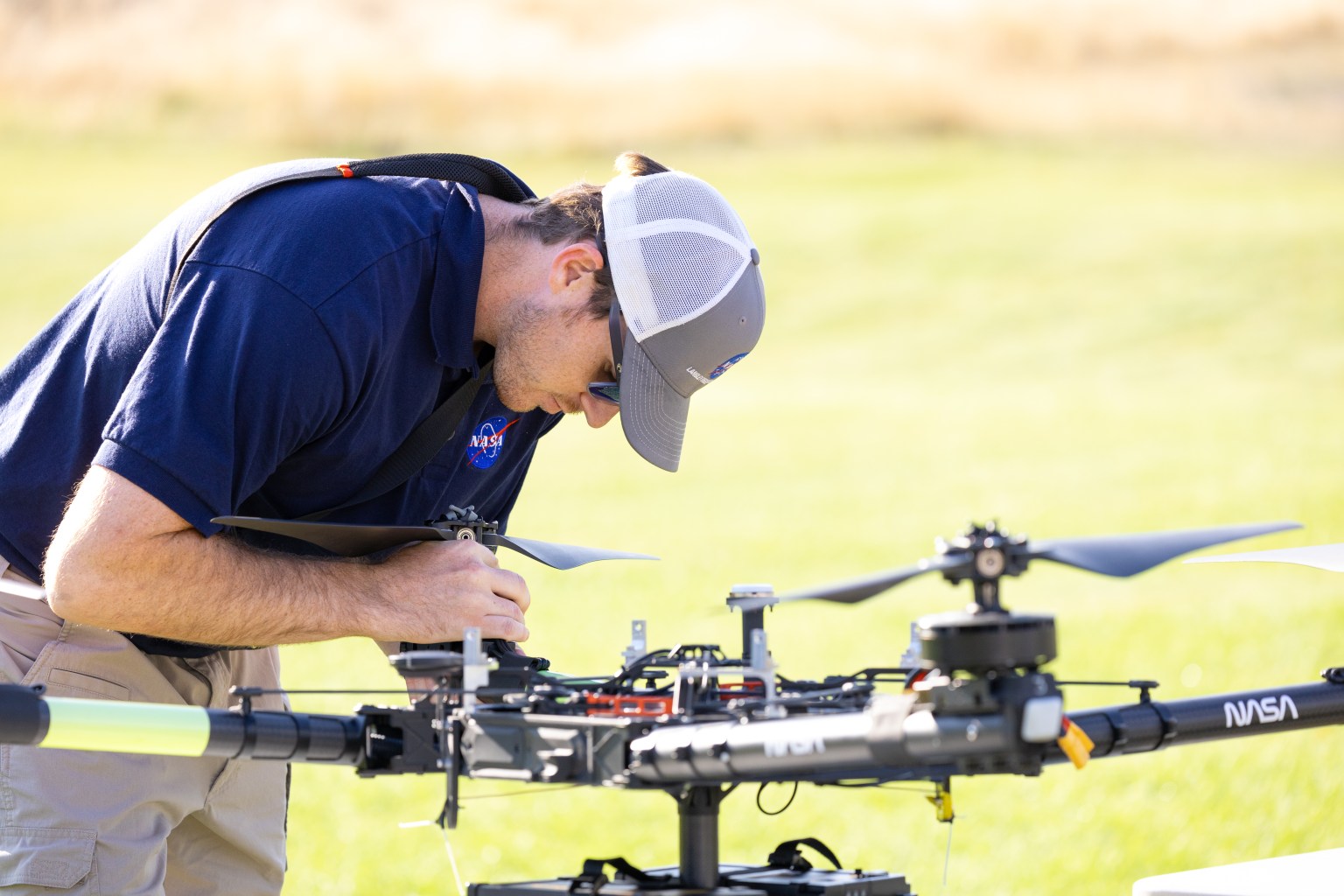
A drone team out of NASA Langley conducted eight data-collection flights in Missoula. Before each drone flight, student teams from the University of Idaho in Moscow, Idaho, and Salish Kootenai College in Pablo, Montana, launched a weather balloon carrying the same type of radiometer.
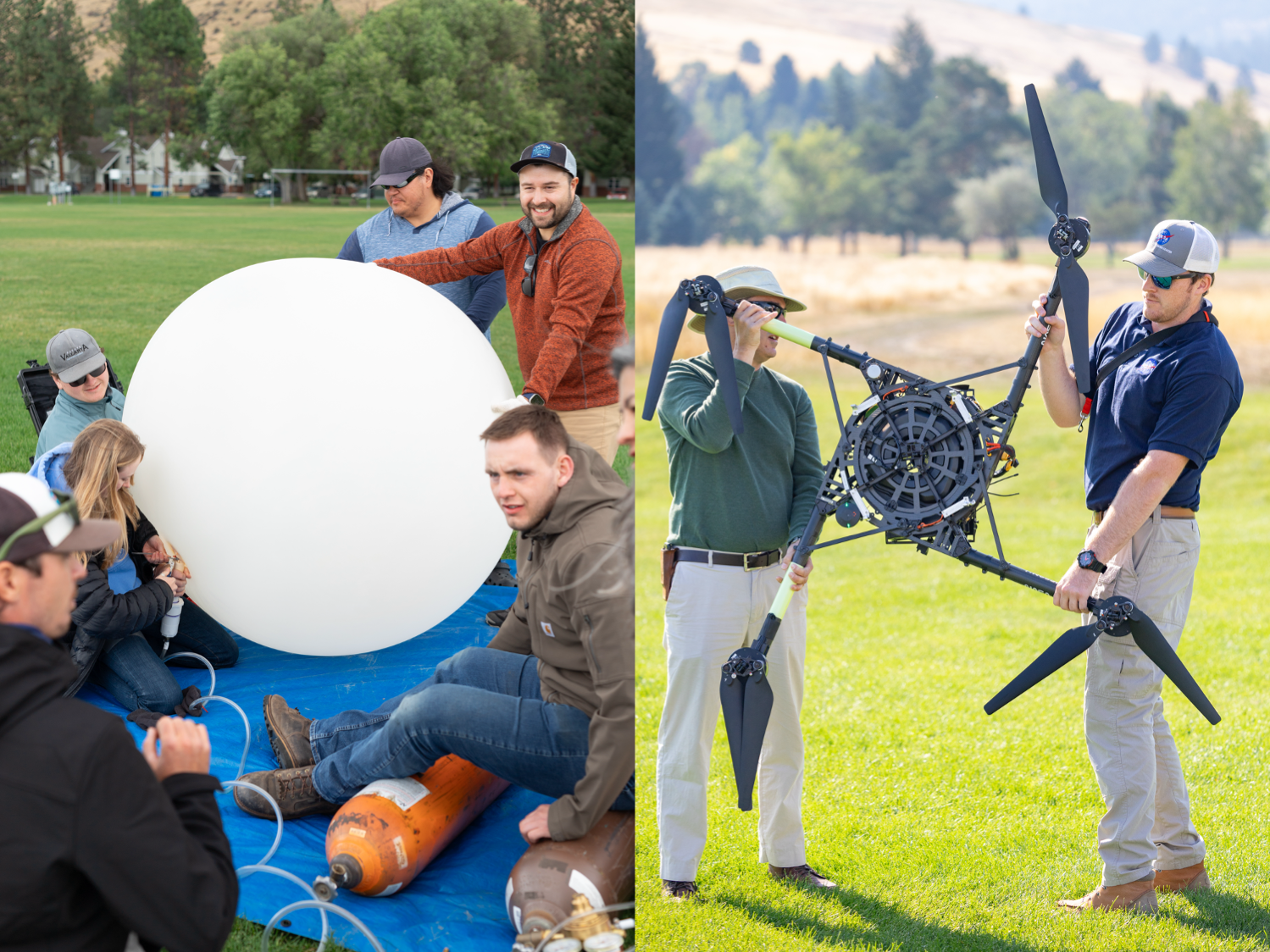

Right: NASA Langley drone crew members Todd Ferrante (left) and Brayden Chamberlain (right) calibrate the internal sensors of the NASA Alta X quadcopter before its first test flight on Aug. 27, 2024.
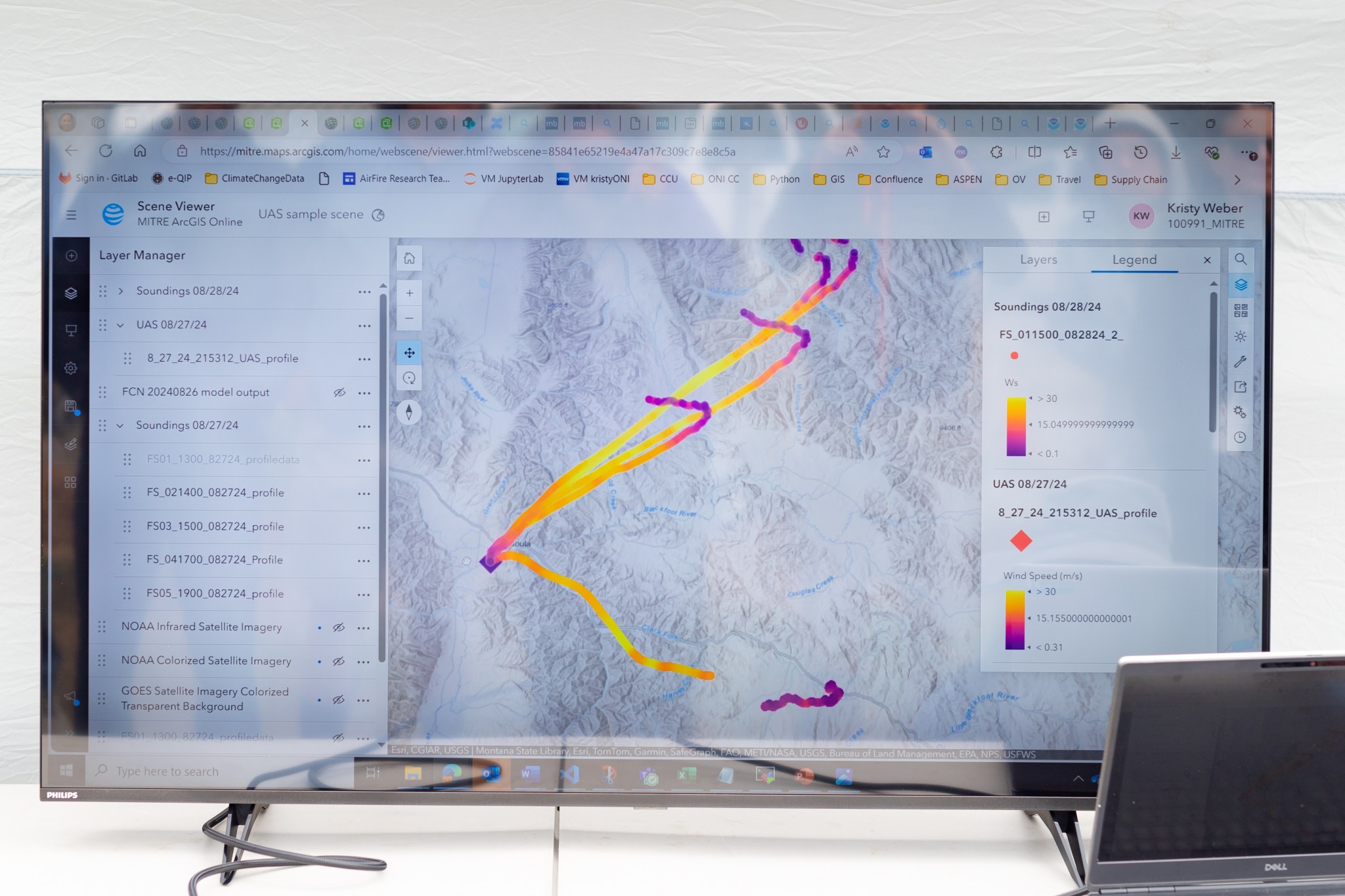
Once those data sets were created, they needed to be transformed into a usable format. Meteorologists are used to the numbers, but incident commanders on an active fire need to see the data in a form that allows them to quickly understand which conditions are changing, and how. That’s where data visualization partners come in. For the Missoula campaign, teams from MITRE, NVIDIA, and Esri joined NASA in the field.
Measurements from both the balloon and the drone platforms were immediately sent to the on-site data teams. The MITRE team, together with NVIDIA, tested high-resolution artificial intelligence meteorological models, while the Esri team created comprehensive visualizations of flight paths, temperatures, and wind speed and direction. These visual representations of the data make conclusions more immediately apparent to non-meteorologists.
What’s Next?
Development of drone capabilities for fire monitoring didn’t begin in Missoula, and it won’t end there.
“This campaign leveraged almost a decade of research, development, engineering, and testing,” said McSwain. “We have built up a UAS flight capability that can now be used across NASA.”
This campaign leveraged almost a decade of research, development, engineering, and testing. We have built up a UAS flight capability that can now be used across NASA.

Robert Mcswain
FireSense Uncrewed Aerial System (UAS) Lead
The NASA Alta X and its sensor payload will head to Alabama and Florida in spring 2025, incorporating improvements identified in Montana. There, the team will perform another technology demonstration with wildland fire managers from a different region.
To view more photos from the FireSense campaign visit: https://nasa.gov/firesense
The FireSense project is led by NASA Headquarters in Washington and sits within the Wildland Fires program, with the project office based at NASA Ames. The goal of FireSense is to transition Earth science and technological capabilities to operational wildland fire management agencies, to address challenges in U.S. wildland fire management before, during, and after a fire.




































































.jpg)

















































![The breaking news round-up: Decagear launches today, Pimax announces new headsets, and more! [APRIL FOOL’S]](https://i0.wp.com/skarredghost.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/lawk_glasses_handson.jpg?fit=1366%2C1025&ssl=1)
























