Hubble Captures a Neighbor’s Colorful Clouds
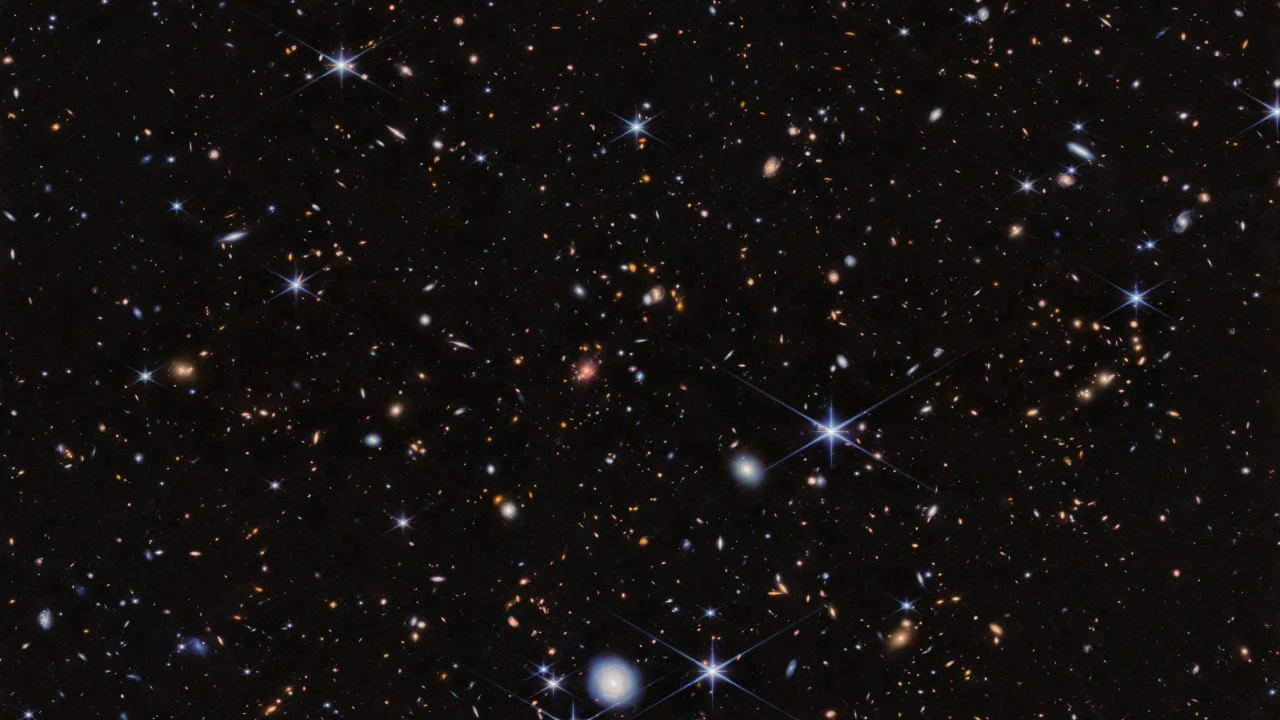
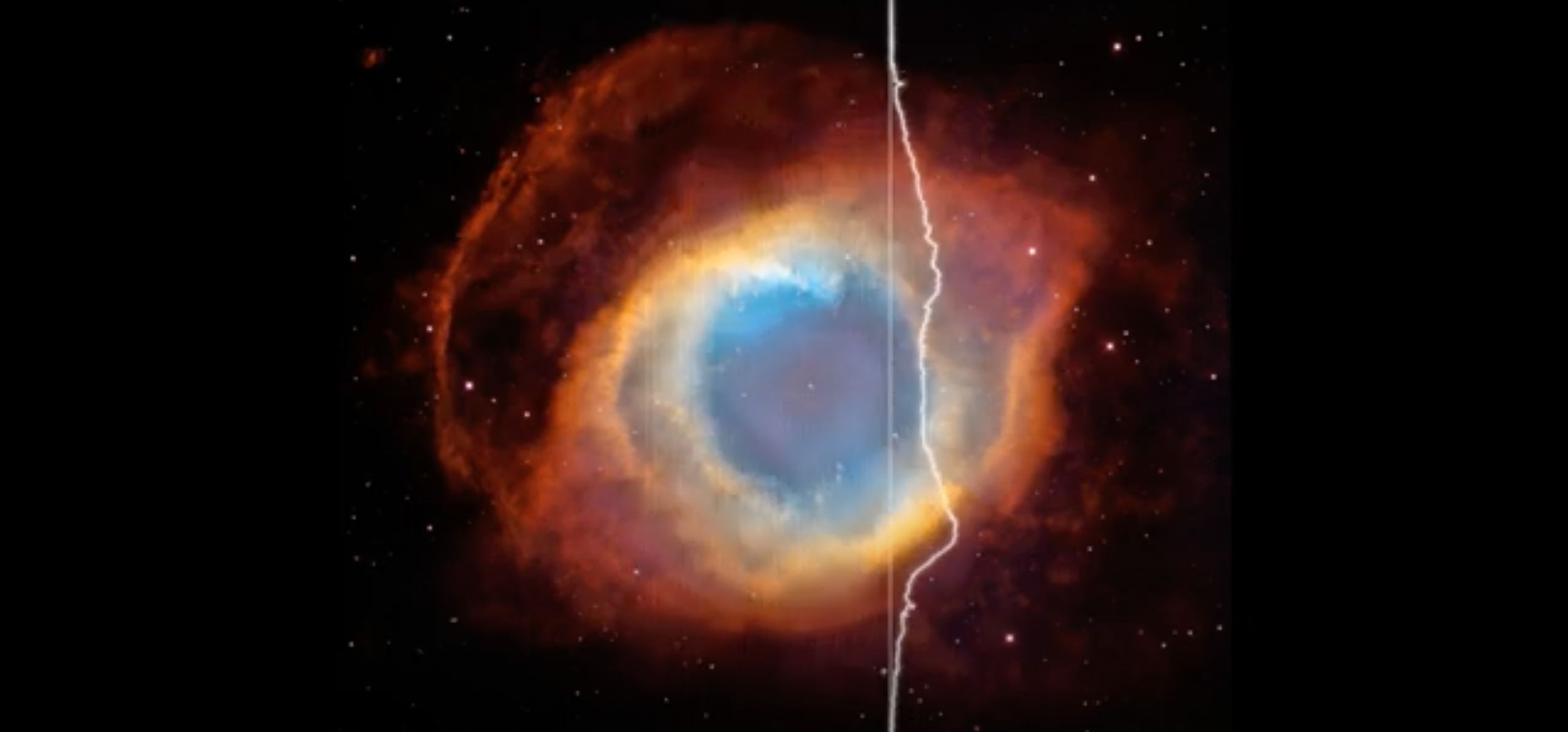
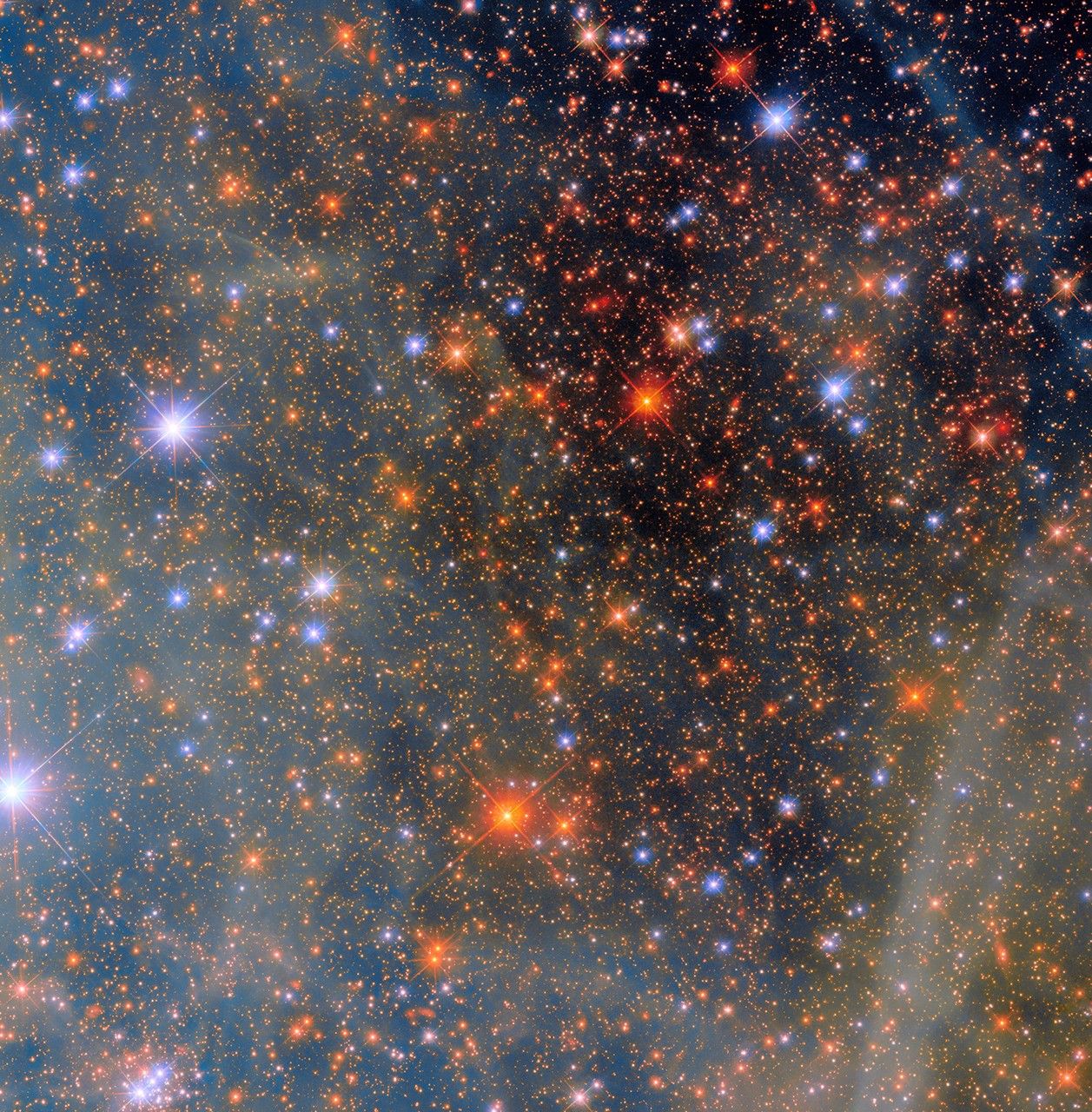
Say hello to one of the Milky Way’s neighbors! This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image features a scene from one of the closest galaxies to the Milky Way, the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC). The SMC is a dwarf galaxy located about 200,000 light-years away. Most of the galaxy resides in the constellation Tucana, but a […]

2 min read
Hubble Captures a Neighbor’s Colorful Clouds
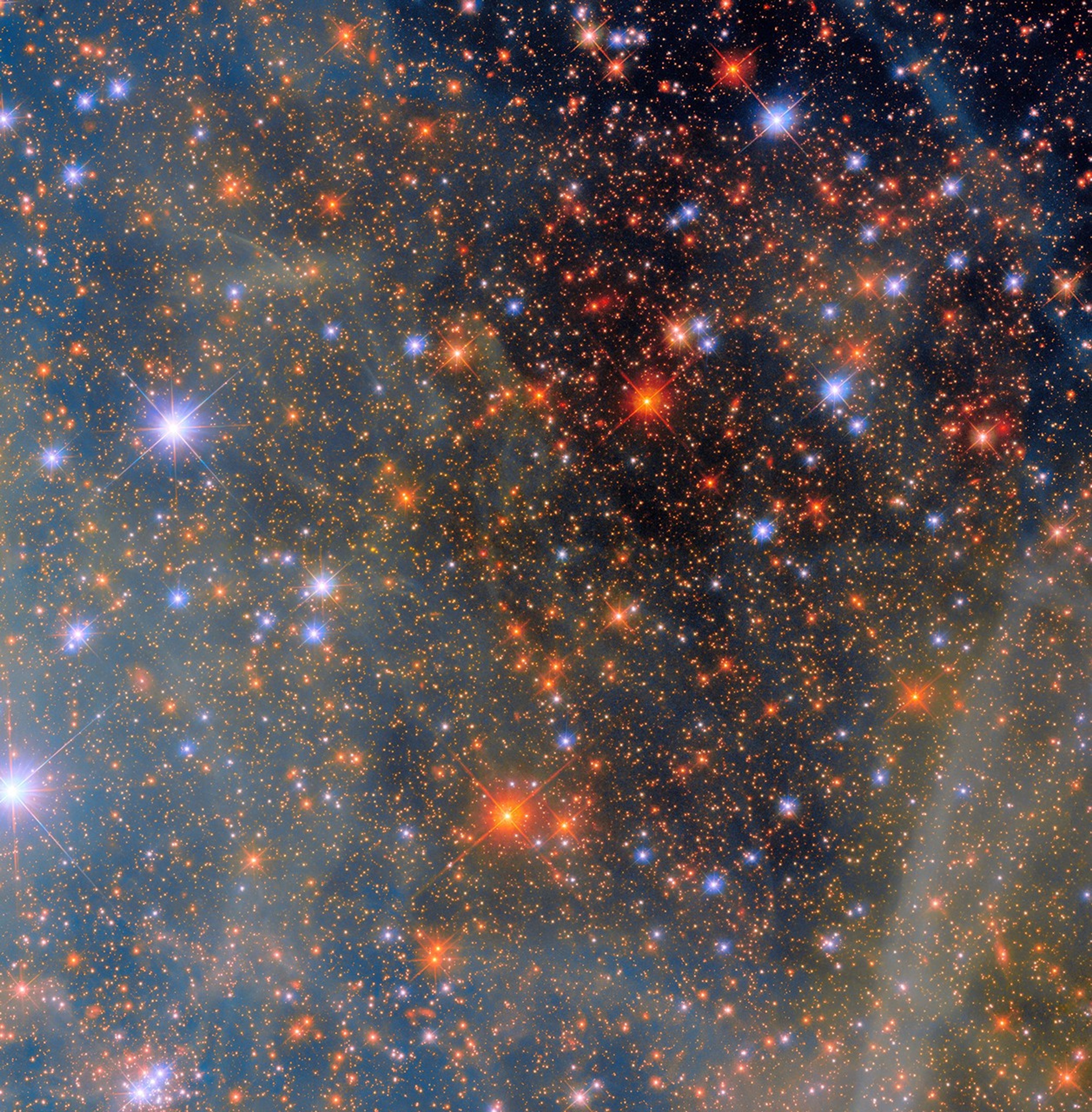
Say hello to one of the Milky Way’s neighbors! This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image features a scene from one of the closest galaxies to the Milky Way, the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC). The SMC is a dwarf galaxy located about 200,000 light-years away. Most of the galaxy resides in the constellation Tucana, but a small section crosses over into the neighboring constellation Hydrus.
Thanks to its proximity, the SMC is one of only a few galaxies that are visible from Earth without the help of a telescope or binoculars. For viewers in the southern hemisphere and some latitudes in the northern hemisphere, the SMC resembles a piece of the Milky Way that has broken off, though in reality it’s much farther away than any part of our own galaxy.
With its 2.4-meter mirror and sensitive instruments, Hubble’s view of the SMC is far more detailed and vivid than what humans can see. Researchers used Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 to observe this scene through four different filters. Each filter permits different wavelengths of light, creating a multicolored view of dust clouds drifting across a field of stars. Hubble’s view, however, is much more zoomed-in than our eyes, allowing it to observe very distant objects. This image captures a small region of the SMC near the center of NGC 346, a star cluster that is home to dozens of massive young stars.
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli (claire.andreoli@nasa.gov)
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD