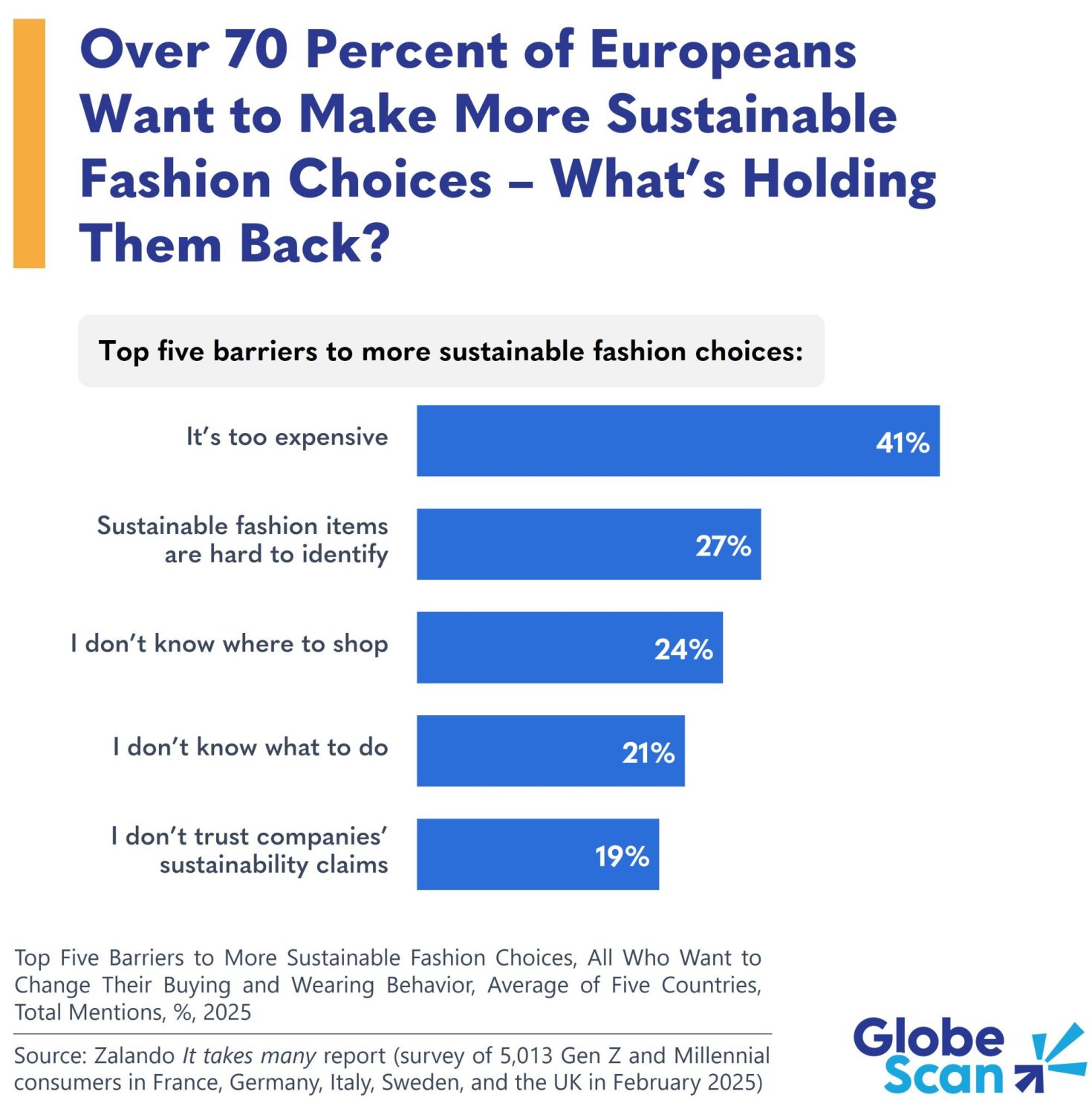
Frozen in time: Transparent worms keep genes in sync for 20 million years
Even after 20 million years of evolutionary separation, two tiny worm species show astonishingly similar patterns in how they turn genes on and off. Scientists mapped every cell s activity during development and found that genes essential to basic functions like muscles and digestion remained largely unchanged. Meanwhile, genes linked to sensing the environment or brain-like functions showed more variation. This high-resolution comparison of every cell between species may help unlock mysteries of how life evolves and adapts without always changing how it looks.