EU’s carbon pricing scheme lowers emissions to 50% of 2005 levels
The numbers demonstrate the success of economic policies focused on climate mitigation. The post EU’s carbon pricing scheme lowers emissions to 50% of 2005 levels appeared first on Trellis.

Key takeaways
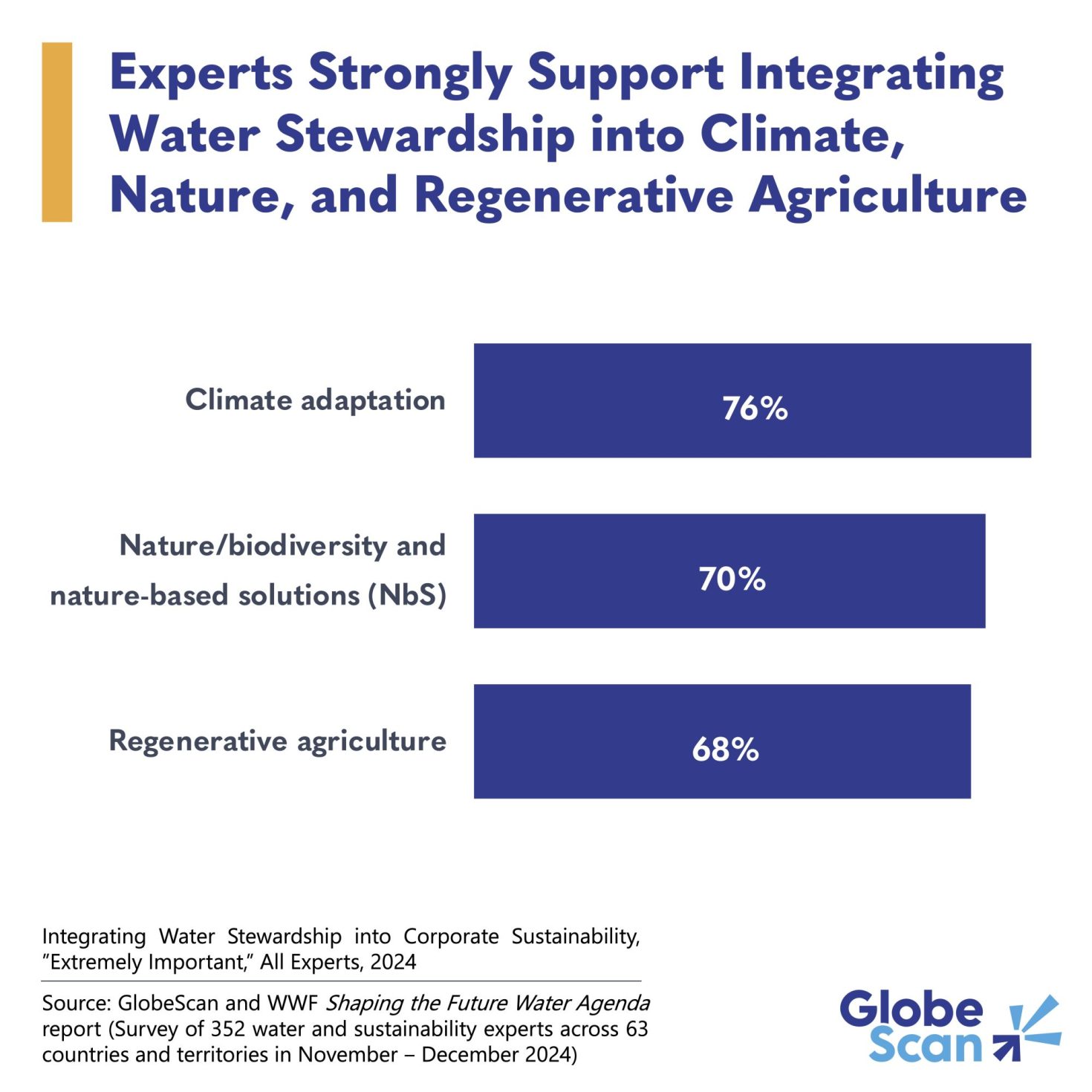
- The EU’s cap-and-trade scheme — the Emissions Trading System (ETS) — released data showing that participating sectors have reduced emission to 50 percent of 2005 levels.
- The reductions keep the EU on track to meet its 62 percent emissions decrease by 2030 goal — thanks, in large part, to a 12 percent emissions reduction seen in the power sector.
- The ETS’s progress proves climate mitigation economics can be a success, right as the EU has been slowly shifting right after its 2024 elections.
The European Union’s oft-criticized Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) has reduced emissions from participating sectors by 50 percent, according to new data, in the process helping the EU stay on track to achieve its 2030 target of lowering emissions by 62 percent.
The assigns a cap to the carbon dioxide produced by companies, while creating incentives to reduce those emissions. EU ETS is similar to cap-and-trade laws established in U.S. states, including like Washington and California. European companies purchase a set amount of emission allowances that covers their expected emissions for one year. If a company emits more than its allotted allowances, it must either purchase allowances from other companies that came in under their cap, or pay a fine.
The price of carbon is set by the market, as companies buy and sell allowances.
As of March 31, 2025, sectors covered by the system demonstrated a 5 percent reduction in total emissions in 2024, compared to 2023 levels, cutting ETS emissions to around half of 2005 levels.
The sectors covered include:
- Electricity generation: The leading sector in decreasing emissions, power producers reduced emissions by 12 percent below 2023 levels, driven mostly by increased renewable energy.
- Industry: The most wide-reaching of the categories, this category includes the energy-intensive production of fertilizer and cement, among others. Industry emissions remained stable from 2023 to 2024.
- Aviation: The only category to see a rise in emissions, aviation increased by 15 percent compared to 2023, likely due to the re-inclusion of non-domestic flights recently added under ETS rules.
- Maritime: The newest sector to enter the system lacks previous data on emissions for comparison.
A time of change
This success happens during a time of change within the EU. The European Parliament recently voted to delay its compliance timeline for the seminal Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD), pushing back the 2026 and 2027 dates to 2028 and 2029.
Meanwhile, elections in the summer of 2024 saw the makeup of EU representatives shift to the right. Far-right groups from Germany, France, and Italy among others gained 189 seats in the EU, more than a quarter of the total.
The post EU’s carbon pricing scheme lowers emissions to 50% of 2005 levels appeared first on Trellis.






















































































































![The breaking news round-up: Decagear launches today, Pimax announces new headsets, and more! [APRIL FOOL’S]](https://i0.wp.com/skarredghost.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/lawk_glasses_handson.jpg?fit=1366%2C1025&ssl=1)