Devil’s in Details in Selfie Taken by NASA’s Mars Perseverance Rover
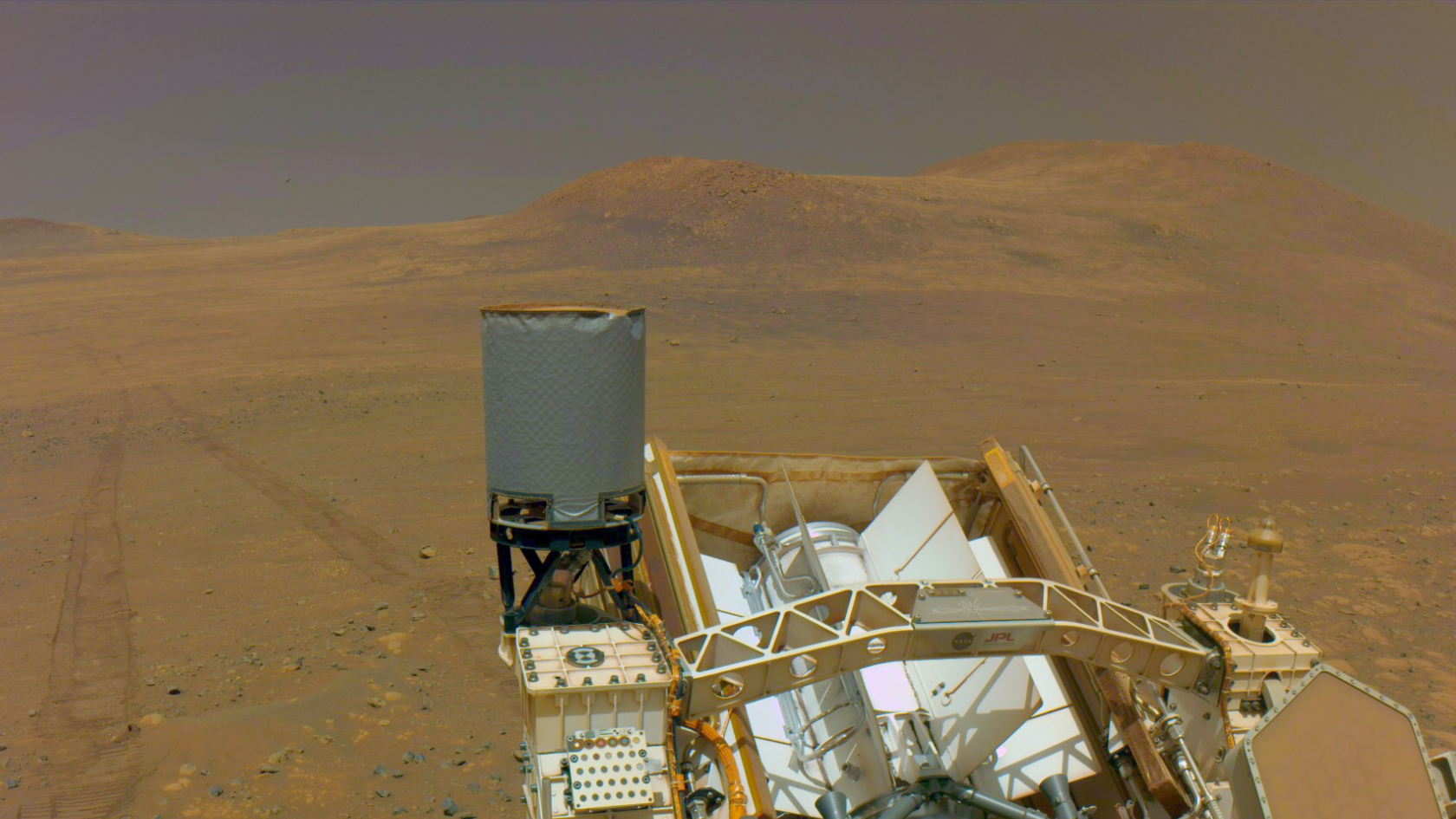
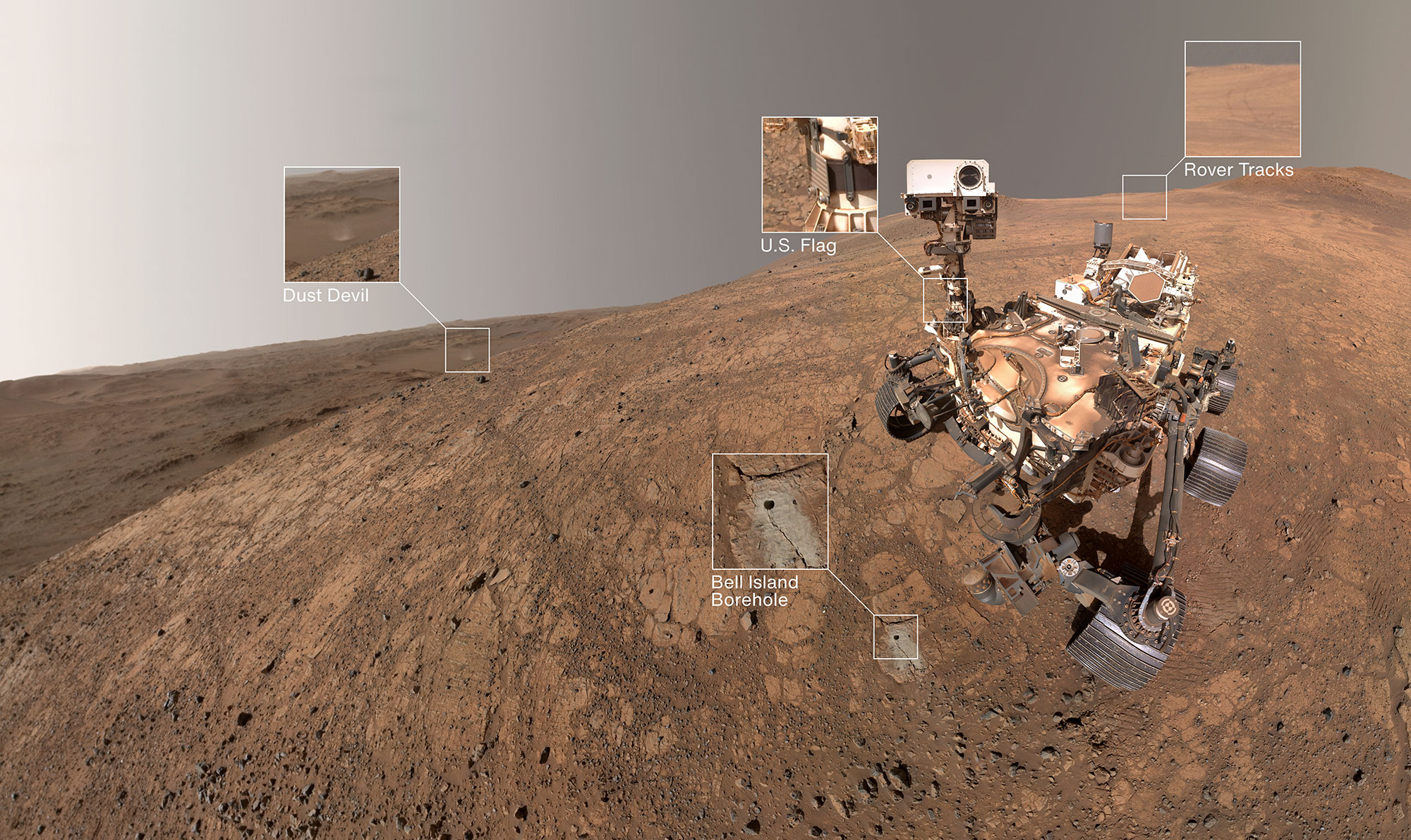
The rover took the image — its fifth since landing in February 2021 — between stops investigating the Martian surface. A Martian dust devil photobombed NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover as it took a selfie on May 10 to mark its 1,500th sol (Martian day) exploring the Red Planet. At the time, the six-wheeled rover was […]
3 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
The rover took the image — its fifth since landing in February 2021 — between stops investigating the Martian surface.
A Martian dust devil photobombed NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover as it took a selfie on May 10 to mark its 1,500th sol (Martian day) exploring the Red Planet. At the time, the six-wheeled rover was parked in an area nicknamed “Witch Hazel Hill,” an area on Jezero Crater’s rim that the rover has been exploring over the past five months.
“The rover self-portrait at the Witch Hazel Hill area gives us a great view of the terrain and the rover hardware,” said Justin Maki, Perseverance imaging lead at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which manages the mission. “The well-illuminated scene and relatively clear atmosphere allowed us to capture a dust devil located 3 miles to the north in Neretva Vallis.”
The selfie also gives the engineering teams a chance to view and assess the state of the rover, its instruments, and the overall dust accumulation as Perseverance reached the 1,500-sol milestone. (A day on Mars is 24.6 hours, so 1,500 sols equals 1,541 Earth days.)
The bright light illuminating the scene is courtesy of the high angle of the Sun at the time the images composing the selfie were taken, lighting up Perseverance’s deck and casting its shadow below and behind the chassis. Immediately in front of the rover is the “Bell Island” borehole, the latest sampling location in the Witch Hazel Hill area.
How Perseverance Did It
This newest selfie, Perseverance’s fifth since the mission began, was stitched together on Earth from a series of 59 images collected by the WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) camera at the end of the robotic arm. It shows the rover’s remote sensing mast looking into the camera. To generate the version of the selfie with the mast looking at the borehole, WATSON took three additional images, concentrating on the reoriented mast.
“To get that selfie look, each WATSON image has to have its own unique field of view,” said Megan Wu, a Perseverance imaging scientist from Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. “That means we had to make 62 precision movements of the robotic arm. The whole process takes about an hour, but it’s worth it. Having the dust devil in the background makes it a classic. This is a great shot.”
The dust covering the rover is visual evidence of the rover’s journey on Mars: By the time the image was captured, Perseverance had abraded and analyzed a total of 37 rocks and boulders with its science instruments, collected 26 rock cores (25 sealed and 1 left unsealed), and traveled more than 22 miles (36 kilometers).
“After 1,500 sols, we may be a bit dusty, but our beauty is more than skin deep,” said Art Thompson, Perseverance project manager at JPL. “Our multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator is giving us all the power we need. All our systems and subsystems are in the green and clicking along, and our amazing instruments continue to provide data that will feed scientific discoveries for years to come.”
The rover is currently exploring along the western rim of Jezero Crater, at a location the science team calls “Krokodillen.”
News Media Contacts
DC Agle
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-393-9011
agle@jpl.nasa.gov
Karen Fox / Molly Wasser
NASA Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1600
karen.c.fox@nasa.gov / molly.l.wasser@nasa.gov
2025-073




































































.jpg)