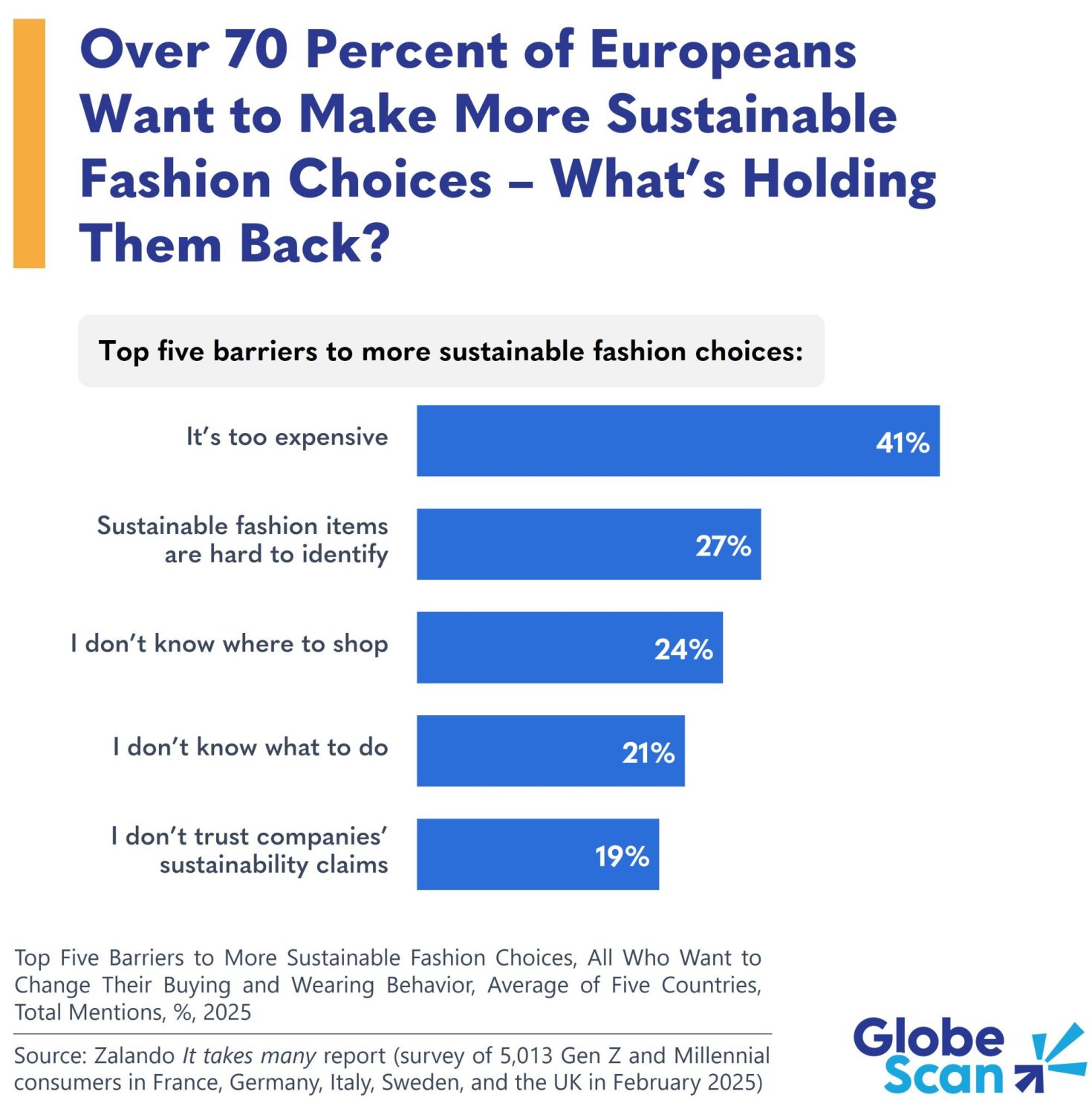
Using the Solar Gravitational Lens Will Be Extremely Difficult
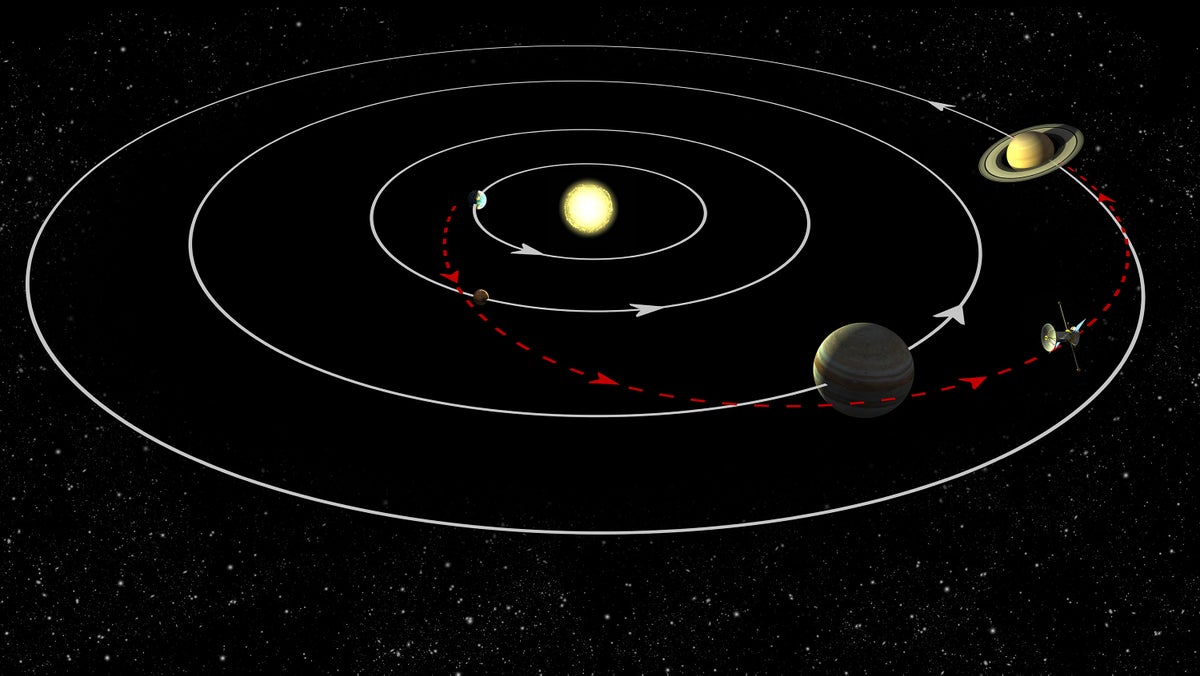
The solar gravitation lens (SGL) has much potential as a telescope. This point in space, located about 650 AU away from the Sun, uses fundamental properties of physics to amplify the light from extremely far-away objects, allowing us to see them at a level of detail unachievable anywhere else. However, any SGL mission would face plenty of technical and physical challenges. A new paper by independent researcher Viktor Toth is the latest in a series that discusses those challenges when imaging a far-away exoplanet, and in particular, looks at the difficulties in dealing with potential moving cloud cover. He concludes that using the SGL might not be the most effective way of capturing high-resolution images of an exoplanet, after all.


The solar gravitation lens (SGL) has much potential as a telescope. This point in space, located about 650 AU away from the Sun, uses fundamental properties of physics to amplify the light from extremely far-away objects, allowing us to see them at a level of detail unachievable anywhere else. However, any SGL mission would face plenty of technical and physical challenges. A new paper by independent researcher Viktor Toth is the latest in a series that discusses those challenges when imaging a far-away exoplanet, and in particular, looks at the difficulties in dealing with potential moving cloud cover. He concludes that using the SGL might not be the most effective way of capturing high-resolution images of an exoplanet, after all.