A CubeSat Propulsion System to Visit Near Earth Objects
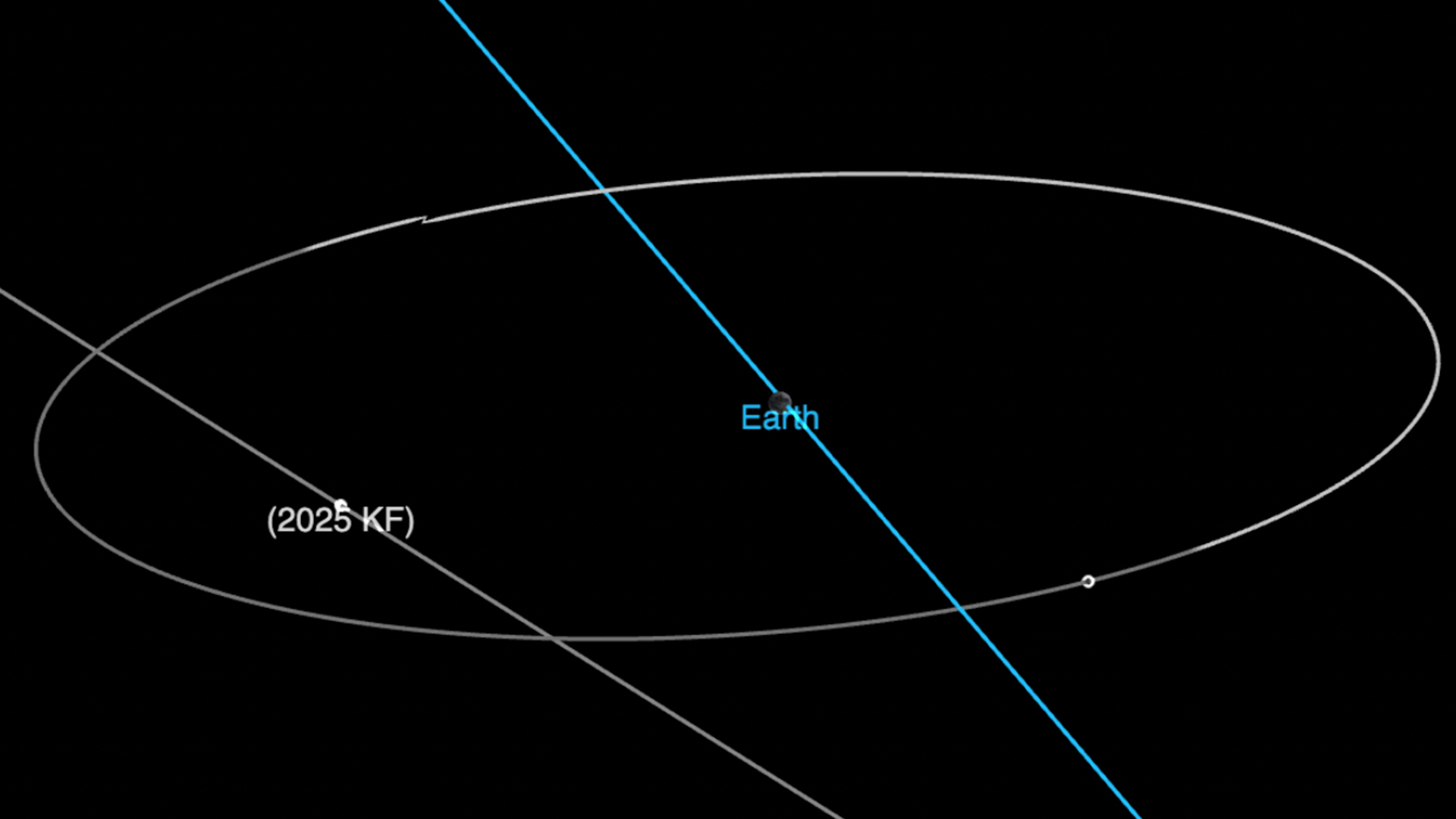
In recent years, humanity has visited several near-Earth asteroids (NEAs), including Ryugu (Hayabusa2) and Didymos (DART). However, we will need more frequent missions to start gathering more helpful information about this class of over 37,000 space rocks. CubeSats have off-the-shelf components and a relatively small size, making them a potentially good candidate for such an exploration program. But how would they reach these asteroid locations given their relatively limited payload and propulsion capacity? That is the focus of a new paper from Alessandro Quarta of the University of Pisa. He looks at potential trajectory planning for CubeSats given one of several configurations of ion drives. He shows how many NEAs can be accessed by simply entering a heliocentric orbit and awaiting the asteroid's arrival as part of its orbit.


In recent years, humanity has visited several near-Earth asteroids (NEAs), including Ryugu (Hayabusa2) and Didymos (DART). However, we will need more frequent missions to start gathering more helpful information about this class of over 37,000 space rocks. CubeSats have off-the-shelf components and a relatively small size, making them a potentially good candidate for such an exploration program. But how would they reach these asteroid locations given their relatively limited payload and propulsion capacity? That is the focus of a new paper from Alessandro Quarta of the University of Pisa. He looks at potential trajectory planning for CubeSats given one of several configurations of ion drives. He shows how many NEAs can be accessed by simply entering a heliocentric orbit and awaiting the asteroid's arrival as part of its orbit.