110 Years Ago: The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics Founded
On March 3, 1915, the United States Congress created the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). Although the NACA’s founding took place just over 11 years after the Wright Brothers’ first powered flightfirst powered flight at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, Congress took the action in response to America lagging behind other world powers’ advances in […]
On March 3, 1915, the United States Congress created the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). Although the NACA’s founding took place just over 11 years after the Wright Brothers’ first powered flightfirst powered flight at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, Congress took the action in response to America lagging behind other world powers’ advances in aviation and aeronautics. From its modest beginnings as an advisory committee, over the years, the NACA established research centers and test facilities that enabled groundbreaking advances in civilian and military aviation, as well as the fledgling discipline of spaceflight. With the creation of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration in 1958, the new agency incorporated the NACA’s facilities, its employees, and its annual budget. The NACA provided NASA with a strong foundation as it set out to explore space.
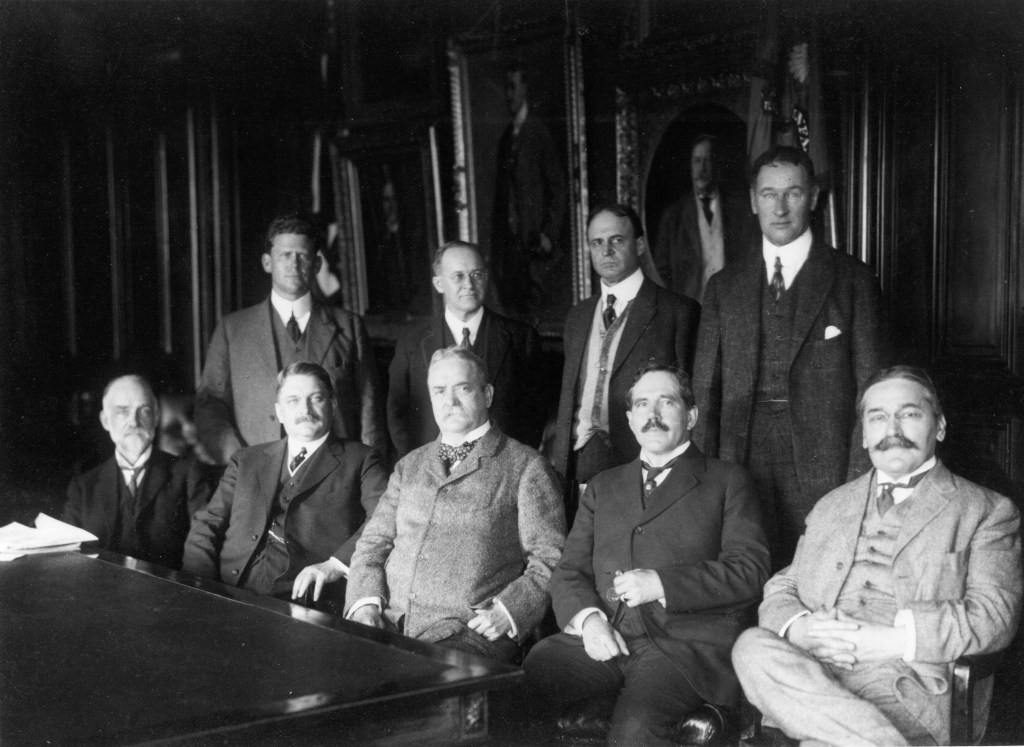
The Congressional action that created the NACA, implemented as a rider to the 1915 Naval Appropriations Bill, reads in part, “…It shall be the duty of the advisory committee for aeronautics to supervise and direct the scientific study of the problems of flight with a view to their practical solution. …”. In its initial years, the NACA fulfilled its intended role, coordinating activities already in place in the area of aeronautics research, reporting directly to the president. The committee, made up of 12 representatives from government agencies, academia, and the military, first met on April 23 in the Office of the Secretary of War in Washington, D.C. It established a nine-member executive committee to oversee day-to-day operations and spent the first few years establishing its headquarters in Washington.
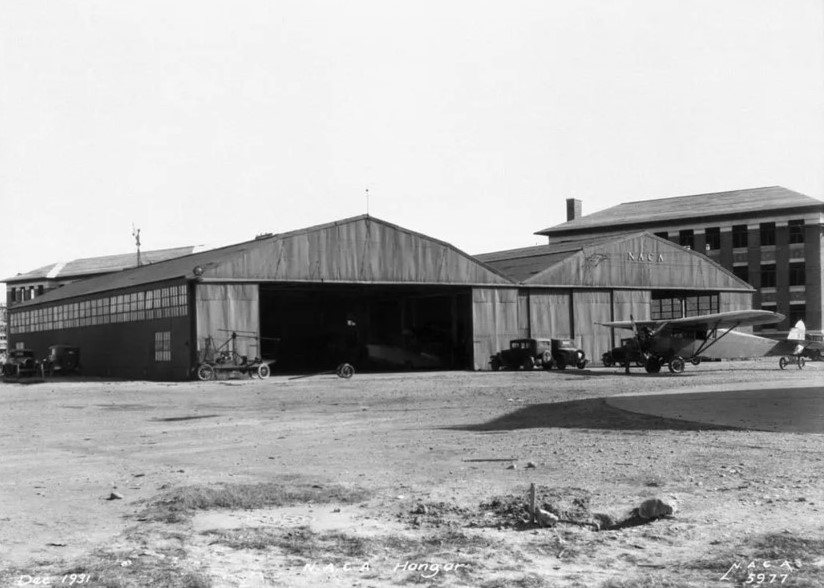
Within a few years, the NACA’s role began to expand with the establishment of research facilities. The Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory, today NASA’s Langley Research Center, in Hampton, Virginia, opened on June 11, 1920. Over the next few decades, Langley served as a testing facility for new types of aircraft, using wind tunnels and other technological advances. The Ames Aeronautical Laboratory in Sunnyvale, California, today NASA’s Ames Research Center, opened in 1940 and the Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory in Cleveland, today NASA’s Glenn Research Center, in 1941. The three labs achieved many breakthroughs in civilian and military aviation before, during, and after World War II. The Cleveland lab, renamed the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in 1948, concentrated most of its efforts on advances in jet propulsion.
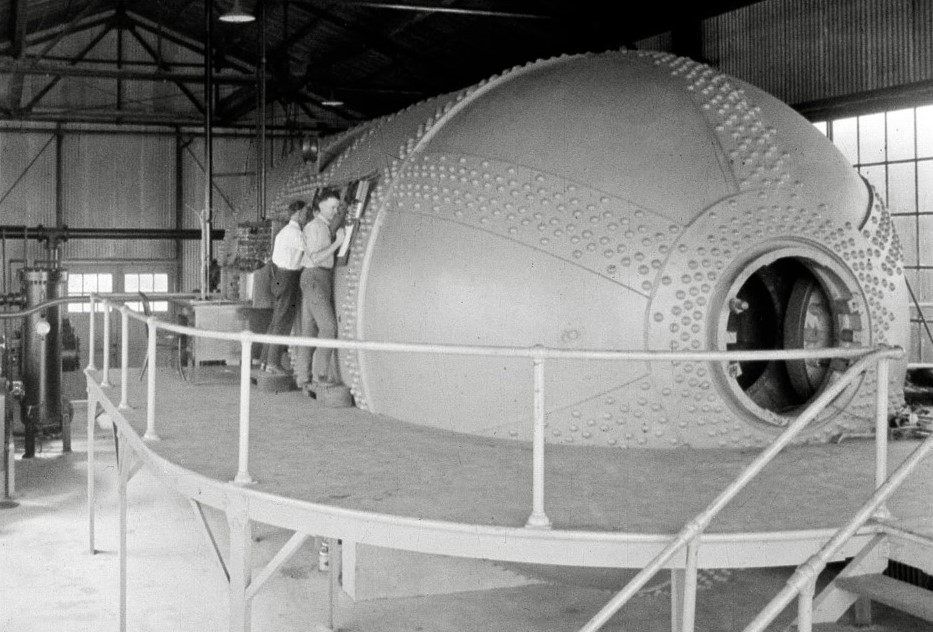
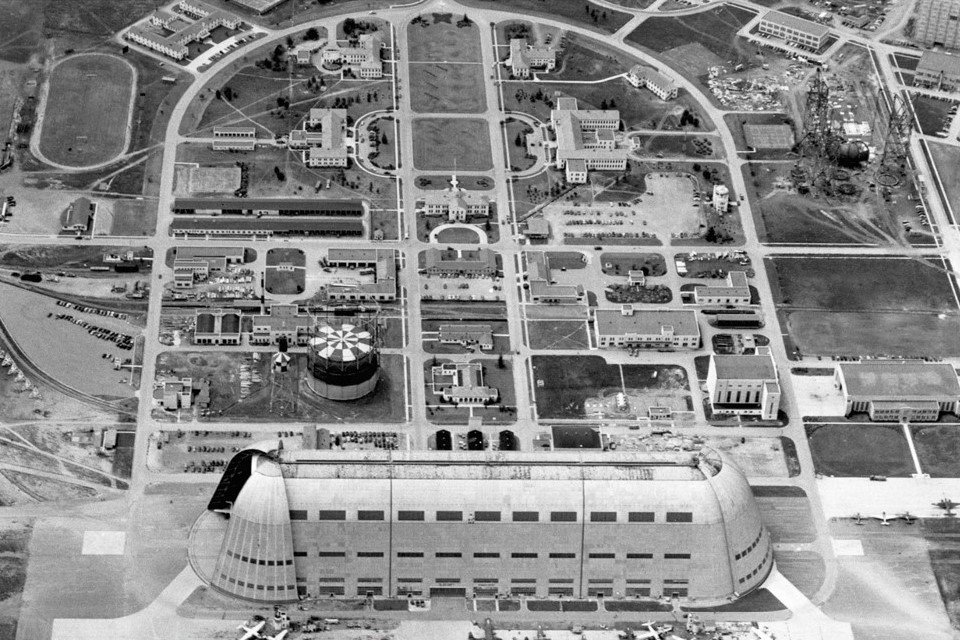
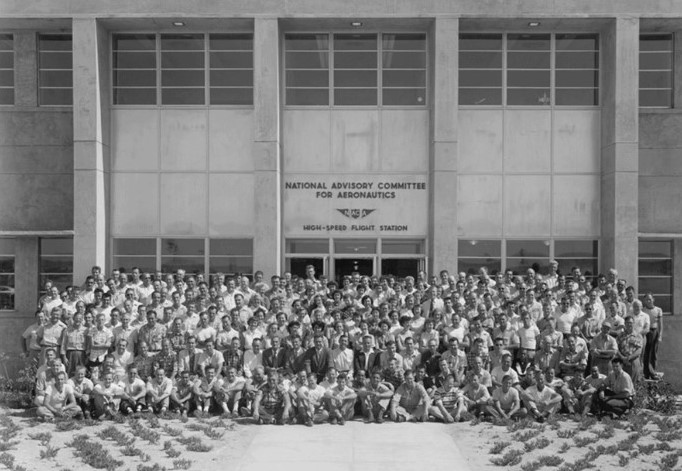
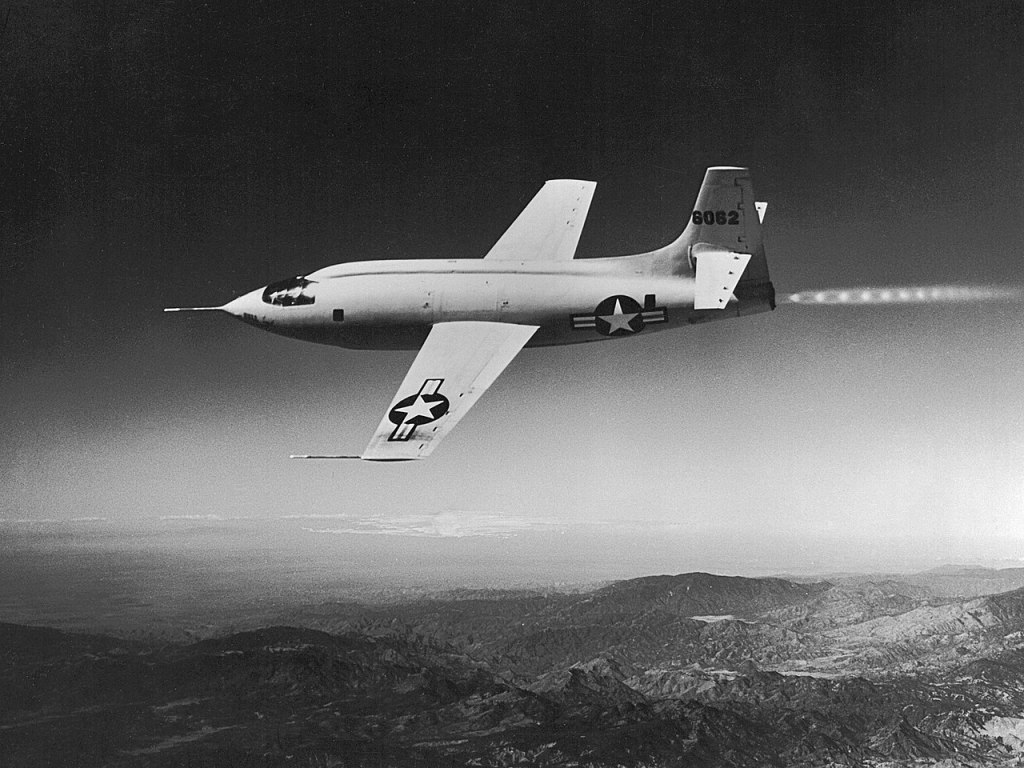
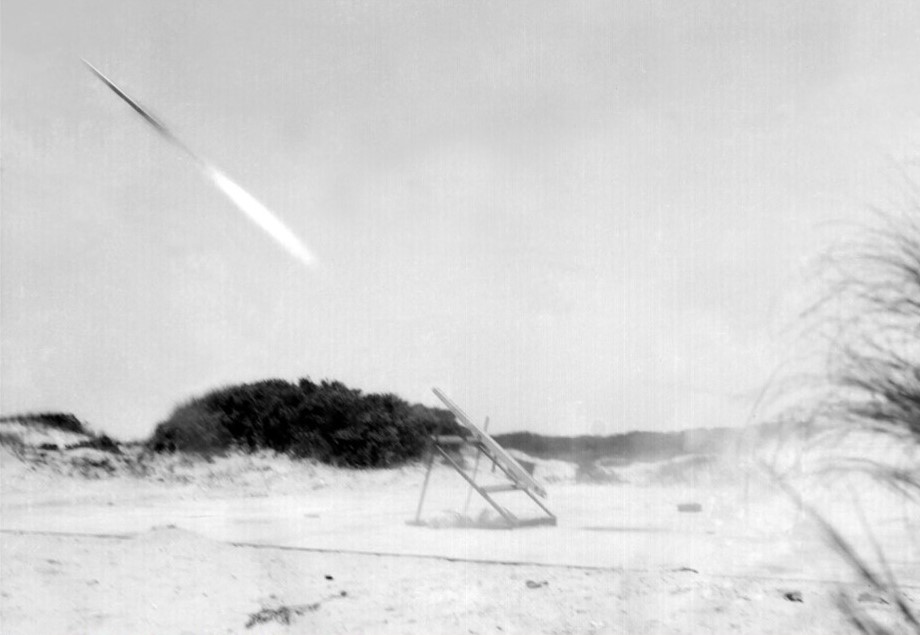
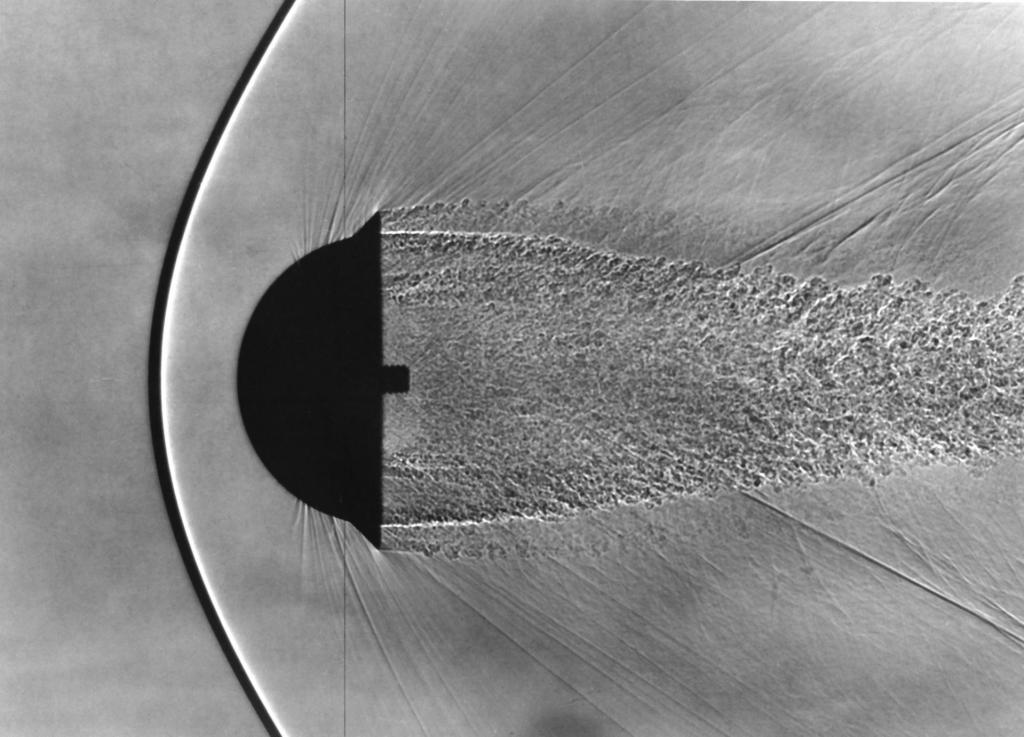
After World War II, the NACA began work on achieving supersonic flight. In 1946, the agency established the Muroc Flight Test Unit at the Air Force’s Muroc Field, later renamed Edwards Air Force Base, in California’s Mojave Desert. In a close collaboration, the NACA, the Air Force, and Bell Aircraft developed the X-1 airplane that first broke the sound barrier in 1947. Muroc Field underwent several name changes, first to the High-Speed Flight Station in 1949, then in 1976 to NASA’s Dryden, and in 2014 to Armstrong Flight Research Center. In 1945, the NACA established the Pilotless Aircraft Research Station on Wallops Island, Virginia, now NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, as a test site for rocketry research, under Langley’s direction. From the first launch in 1945 through 1958, the NACA launched nearly 400 different types of rockets from Wallops.
In the 1950s, the NACA began to study the feasibility of spaceflight, including sending humans into space. In 1952, NACA engineers developed the concept of a blunt body capsule as the most efficient way to return humans from space. The design concept found its way into the Mercury capsule and all future American spacecraft. Following the dawn of the space age in 1957, the NACA advocated that it take the lead in America’s spaceflight effort. The Congress passed, and President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed legislation to create a new civilian space agency, and on Oct. 1, 1958, NASA officially began operations. The new organization incorporated the NACA’s research laboratories and test facilities, its 8,000 employees, and its $100 million annual budget. Many of NASA’s key early leaders and engineers began their careers in the NACA. The NACA’s last director, Hugh Dryden, served as NASA’s first deputy administrator.
For more information about the NACA and its transition to NASA, read former NASA Chief Historian Roger Launius’ book NASA to NASA to Now: The Frontiers of Air and Space in the American Century. Watch this video narrated by former NASA Chief Historian Bill Barry about the NACA.



































































.jpg)













































![The breaking news round-up: Decagear launches today, Pimax announces new headsets, and more! [APRIL FOOL’S]](https://i0.wp.com/skarredghost.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/lawk_glasses_handson.jpg?fit=1366%2C1025&ssl=1)