Wave-dissipating blocks reduce carbon footprint by using oyster shells and c-slurry
Wave-dissipating blocks reduce carbon footprint by using oyster shells and c-slurryWhen you’re on vacation at the beach, you probably enjoy looking at and listening to waves as they crash onto the shore. You may even...


When you’re on vacation at the beach, you probably enjoy looking at and listening to waves as they crash onto the shore. You may even like going into the water and battling these waves, safely of course. But these wave actions can sometimes cause damage on the shore and shoreline structures so we put wave-dissipating blocks to protect them. Most of the materials used here are concrete and cement which are not always suitable for marine life and also contribute to global warming. Two students have come up with a project to use more eco-friendly materials for them.
Designers: Chia-Ying Chiang and Shao-Yu Lin
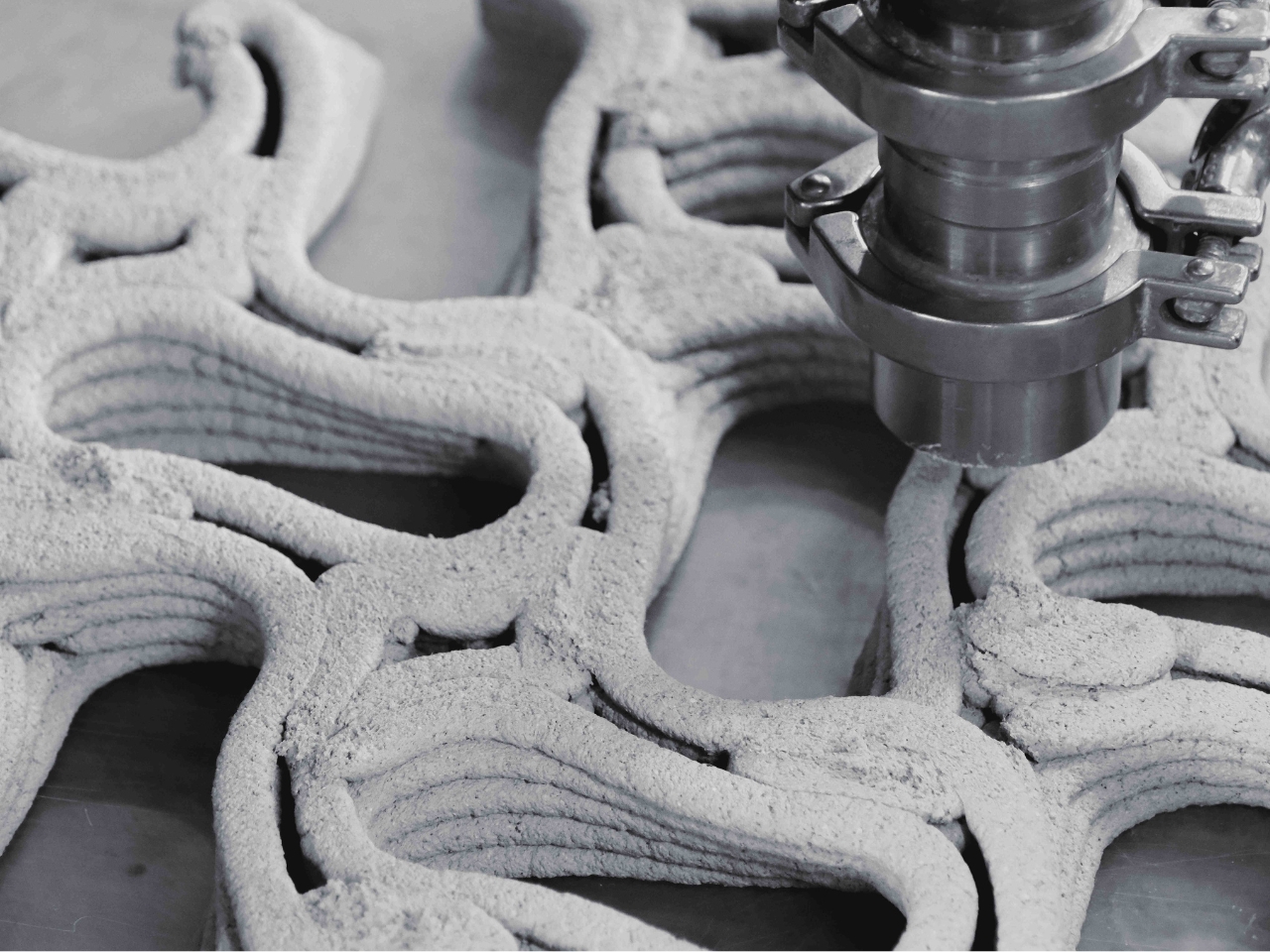
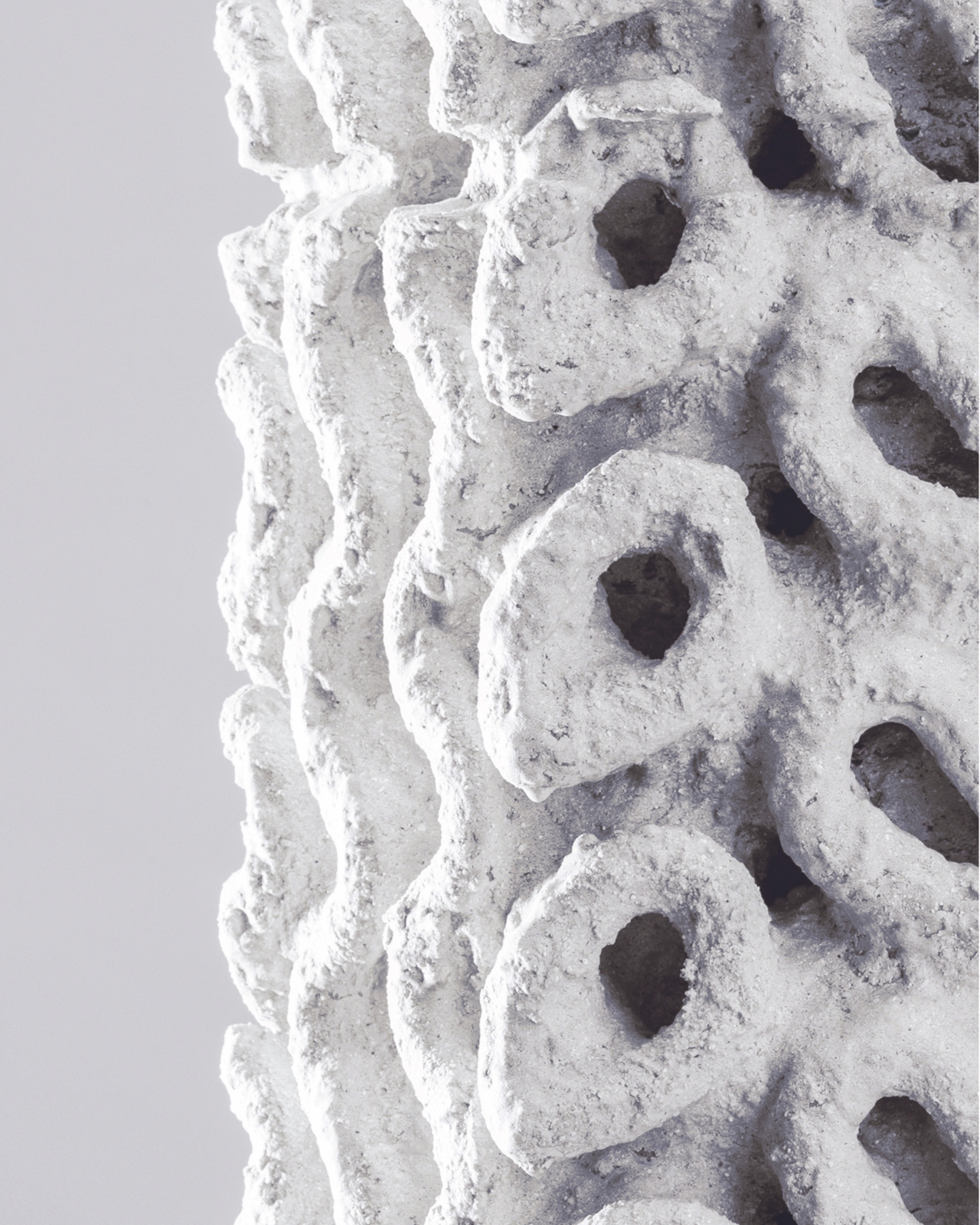


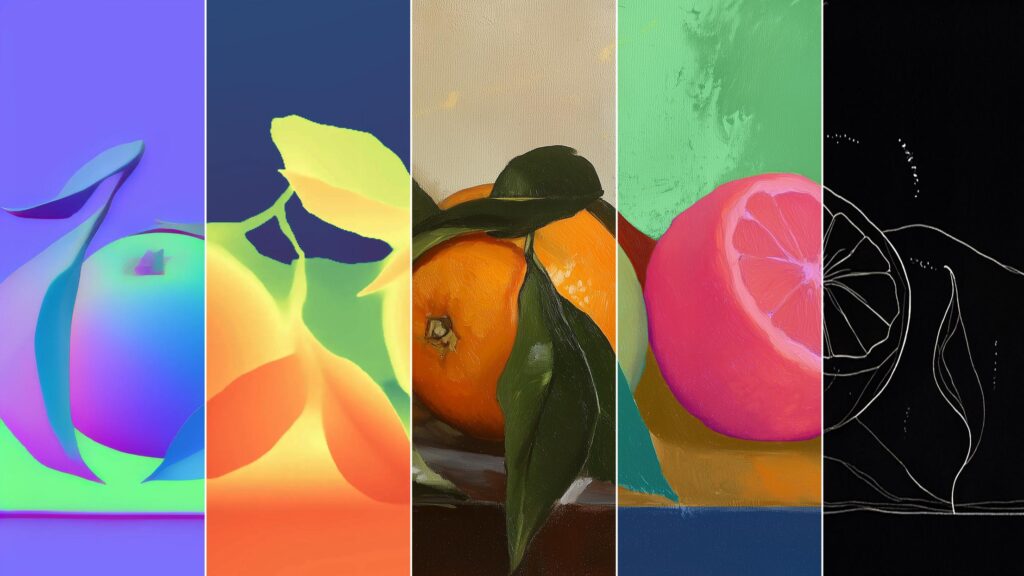
The Ecotrapod is what they call “a new solution to wave dissipation” and this project has won them awards in their homeland of Taiwan. Instead of the usual cement or concrete, they used Circular Slurry of C-slurry mixed together with oyster shells to serve as base materials for the wave-dissipating blocks. The blocks are also structurally designed using biometric principles with bio-porous spiral surfaces. This means they are able to get maximum structural strength aside from reducing carbon emissions by 30-90% since they can reduce or even replace cement.
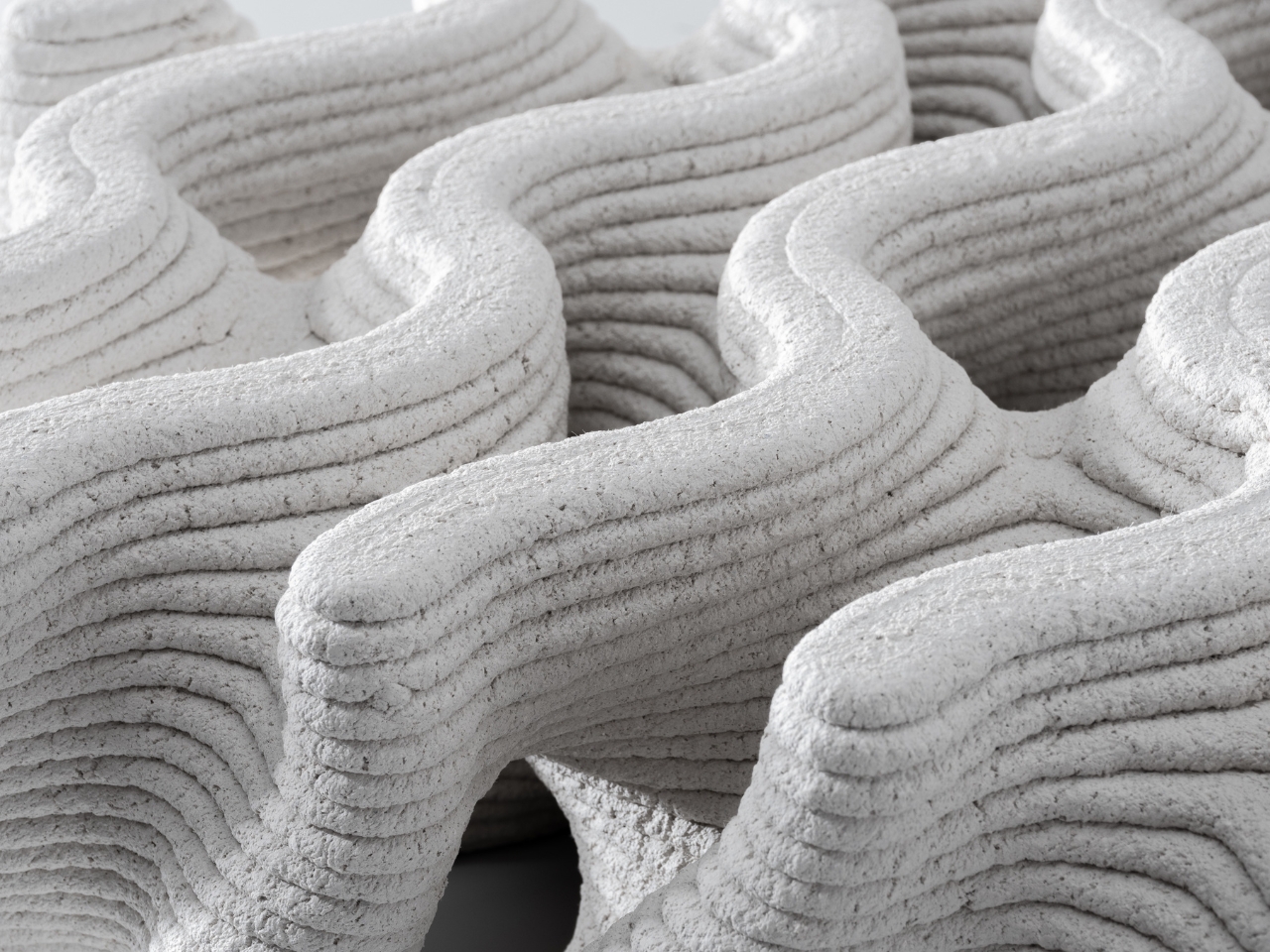
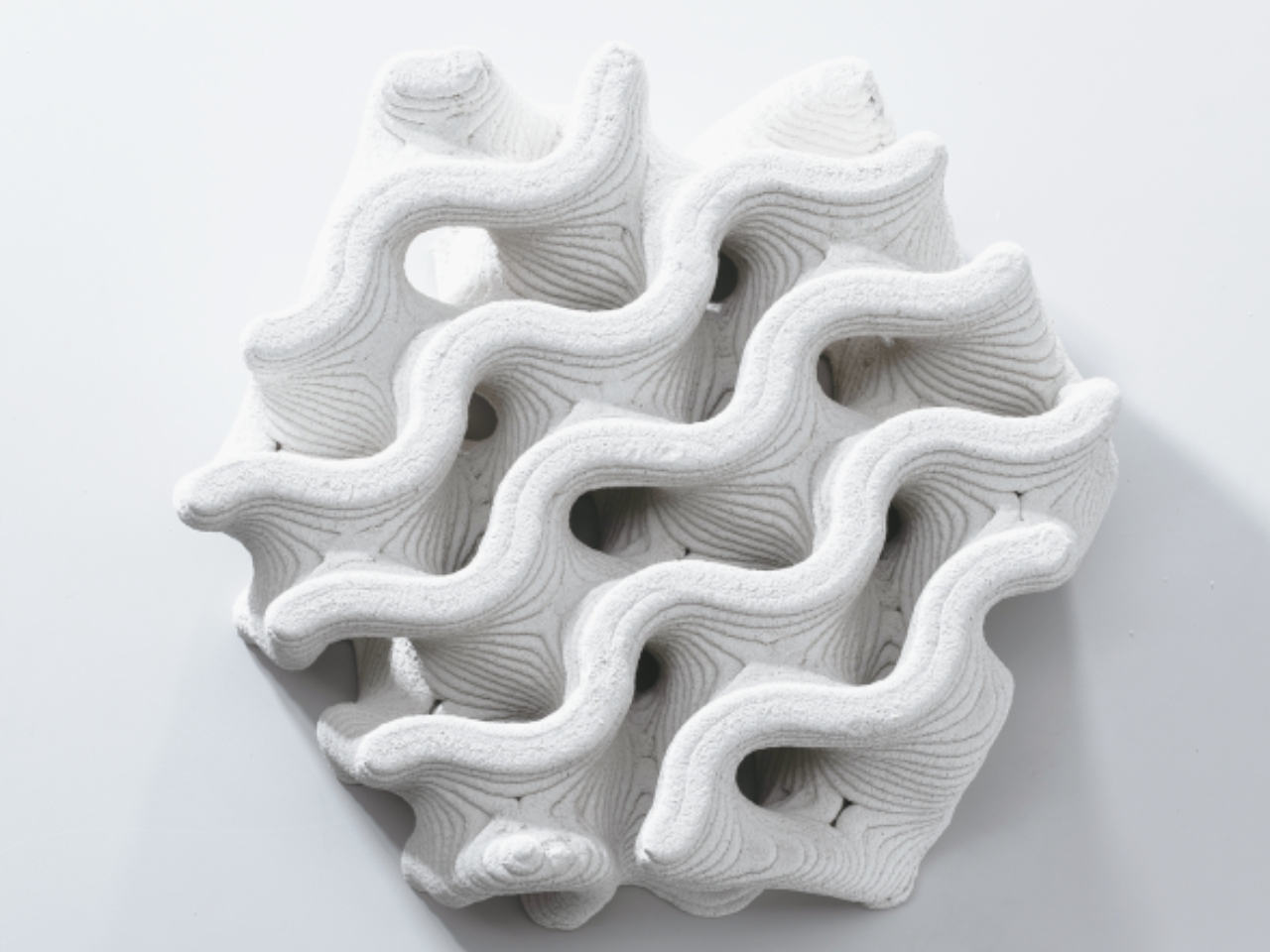


Aside from the more environmentally friendly construction of the blocks, they were also designed with holes so algae can attach themselves to it and some species of fish and shellfish can live within them. This means that aside from protecting the shore, visitors to the ocean can also observe marine ecology within that space, interacting with these coastal organisms. The wavy and porous design of course also makes these blocks seemingly part of the ocean instead of just blocking the waves.
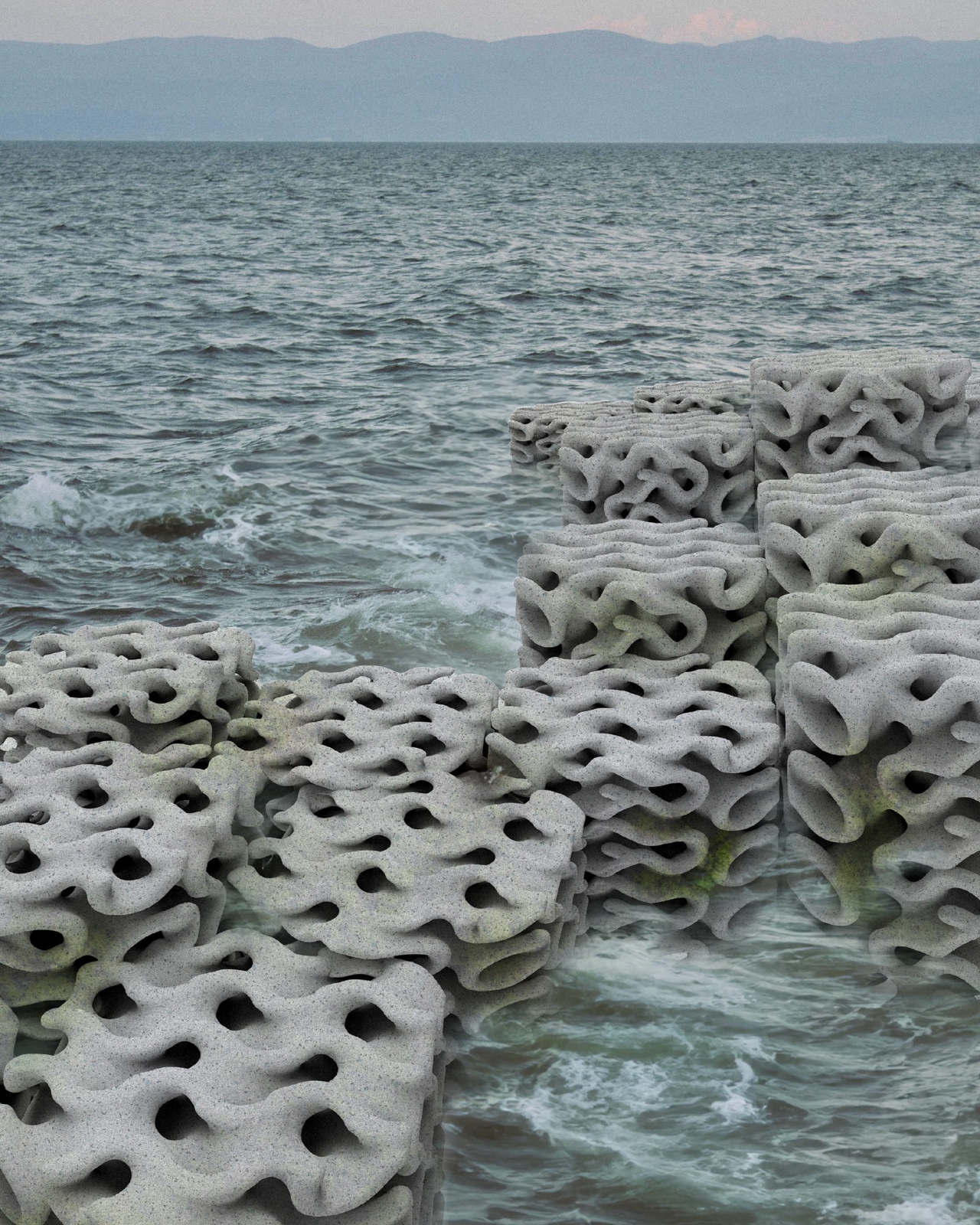

The two designers collaborated with C-Cube, Lotos, and Everplast for this project, which they started and completed since they have a deep love for the ocean and wanted to create sustainable ecological cycles. With the material reducing carbon footprint by 50%, 3D printing can also reduce material usage. Once the blocks have reached the end of their purpose, they can be crushed and then remade into new materials, completing the recycling and reusing cycle.
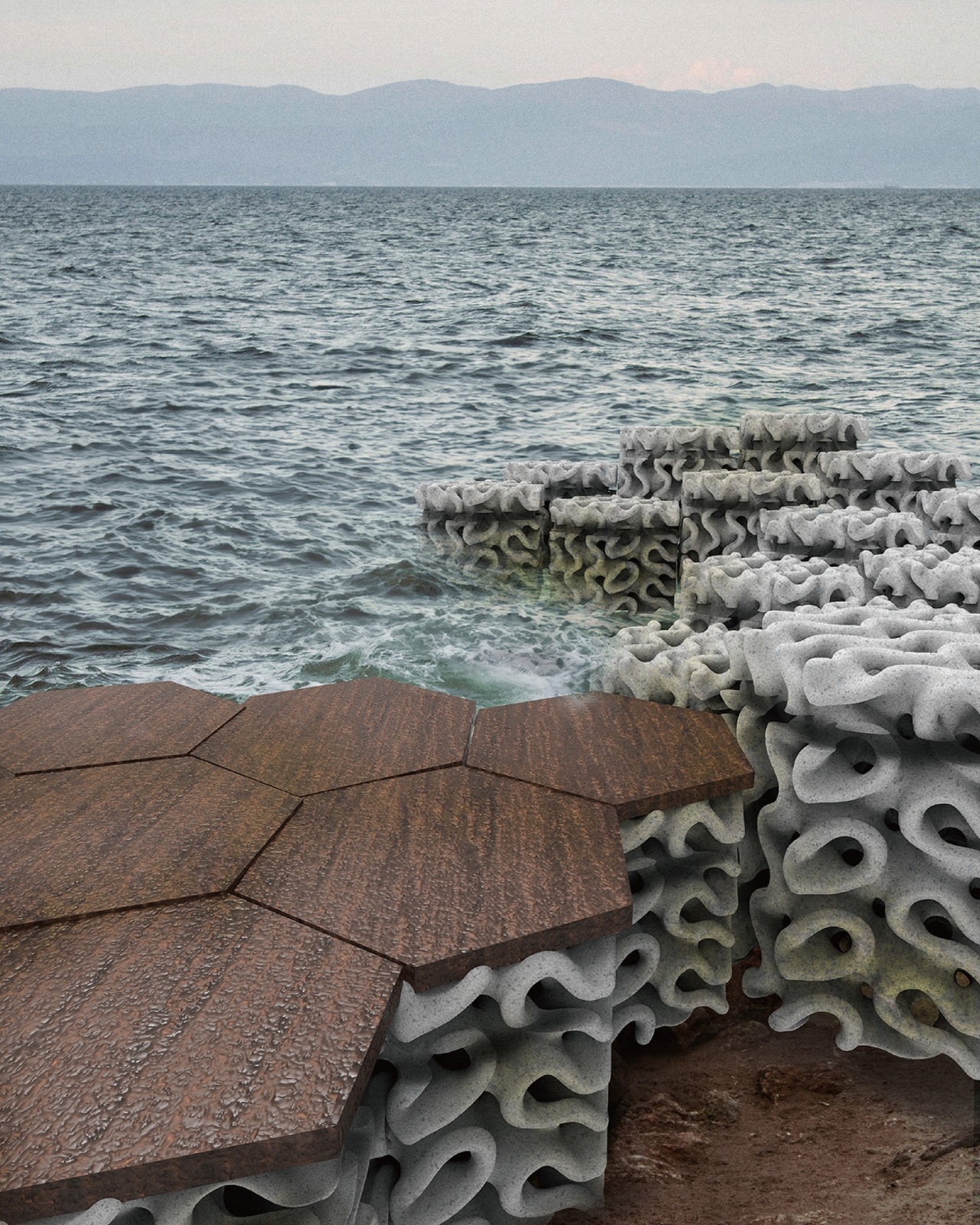

The post Wave-dissipating blocks reduce carbon footprint by using oyster shells and c-slurry first appeared on Yanko Design.
What's Your Reaction?