DME Providers Lead to Better CGM Adherence and Lower Healthcare Costs Compared to Pharmacies
What You Should Know: – New research published in Clinical Diabetes, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Diabetes Association, reveals that patients receiving continuous glucose monitors (CGM) through durable medical equipment (DME) providers demonstrate significantly higher adherence and lower healthcare costs compared to those using pharmacy channels. – The study, titled “Impact of Continuous Glucose ... Read More


What You Should Know:
– New research published in Clinical Diabetes, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Diabetes Association, reveals that patients receiving continuous glucose monitors (CGM) through durable medical equipment (DME) providers demonstrate significantly higher adherence and lower healthcare costs compared to those using pharmacy channels.
– The study, titled “Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Sourcing on Real-World Adherence and Healthcare Costs: A Comparative Analysis by Insurance Type,” challenges the notion that expanding CGM access through pharmacies improves patient outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
Link Between Clinical Glucose Monitor Distribution Channel and Patient Outcomes
CCS, a provider of clinical solutions and home-delivered medical supplies for those living with chronic conditions, conducted this groundbreaking research, which highlights that adding the pharmacy as a new channel for CGM distribution, alongside the established DME provider channel, may be having unintended negative consequences.
While previous studies have shown higher adherence and lower costs with DME providers, this latest research is unique in that it examined differences between commercial and Medicare Advantage insurance populations. The findings highlight that the channel decision for medical supply distribution significantly impacts outcomes and healthcare expenditures.
Key findings from the research include:
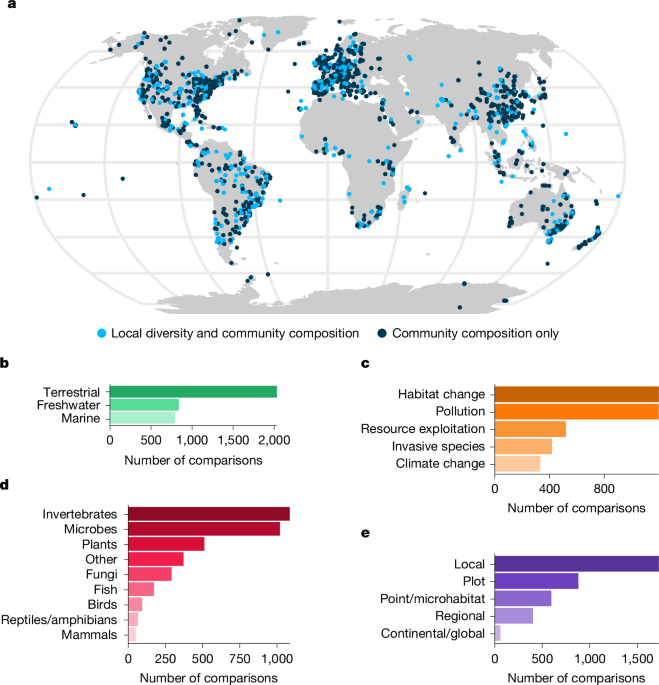
- Improved Adherence: Patients receiving CGM supplies through the DME channel demonstrated greater adherence to their prescribed therapy. At 12 months:
- Medicare/Medicare Advantage patients: 78% adherence with DME vs. 64% with pharmacy.
- Commercially insured patients: 60% adherence with DME vs. 48% with pharmacy.
- Lower Total Costs of Care: Among Medicare and Medicare Advantage patients, total costs of care were 35% lower for those using DME providers.
- At 12 months, patients leveraging the DME channel cost approximately $3,875 less than pharmacy users ($11,154 vs. $15,029).
- Reduced Healthcare Utilization: Commercially insured patients using the DME channel had significantly fewer emergency room (ER) and inpatient (IP) days than those utilizing the pharmacy channel (8 days vs. 11 days).
“This research presents an opportunity to align health plan policies with provider preferences based on measurable outcomes. The data shows patients utilizing DME providers experience higher adherence rates, reduced healthcare costs, and fewer emergency interventions compared to pharmacy channels,” said Dr. Arti Masturzo, Chief Medical Officer at CCS. “By focusing on these evidence-based results, we can work toward building a healthcare system where patients receive better diabetes management support while reducing costs for the entire system.”